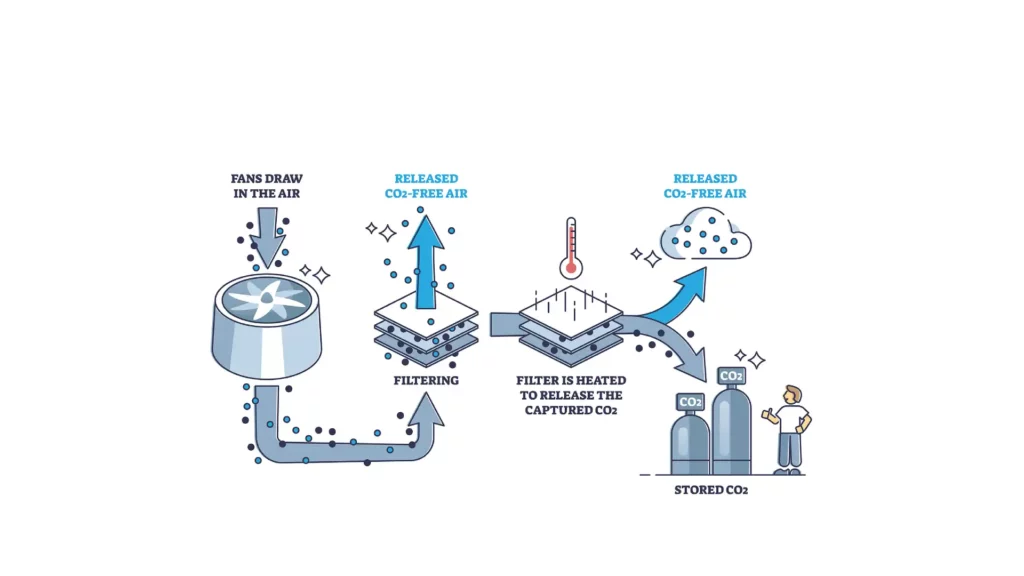
In an era where the battle against climate change is more critical than ever, innovative solutions like Carbon Capture Storage (CCS) have emerged as pivotal technologies.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the myriad advantages of Carbon Capture Storage, underscoring its significance in our collective efforts to mitigate global warming.
With a detailed examination of its applications, benefits, and global impact, we aim to provide insights into how CCS is shaping the future of sustainable energy.
Understanding Carbon Capture Storage
Carbon Capture and Storage a technology at the forefront of environmental innovation, offers a promising path to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
By capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from sources like power plants and industrial facilities, and then transporting it to a storage site where it is injected into deep geological formations for long-term isolation.
CCS plays a crucial role in the fight against climate change.
The Role of CCS in Mitigating Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to our planet, with CO2 emissions from human activities being a major contributor.
The advantages of Carbon Capture Storage are vast, as it addresses this issue head-on by capturing up to 90% of CO2 emissions produced by burning fossil fuels in electricity generation and industrial processes.
The Essential Advantages of Carbon Capture Storage
- Significant Reduction in CO2 Emissions: CCS significantly reduces CO2 emissions from industrial and energy sources, capturing up to 90% of CO2 from fossil fuels, aligning with Paris Agreement goals.
- Facilitates the Transition to Renewable Energy: CCS acts as a bridge to a renewable energy future, allowing cleaner use of fossil fuels while renewable technologies develop.
- Enhances Energy Security: CCS enables the continued use of domestic fossil fuel reserves, reducing dependence on imported energy and managing carbon footprints.
- Economic Benefits and Job Creation: Deployment of CCS technology creates jobs in engineering, construction, and operation, stimulating industries related to CO2 storage and transportation.
- Enables Negative Emissions: Technologies like BECCS can achieve negative emissions, removing more CO2 from the atmosphere than emitted, crucial for long-term climate goals.
- Versatility and Scalability: CCS can be applied to a wide range of CO2 sources, including power plants and industrial processes, offering flexibility in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Promotes Technological Innovation and Development: Research and deployment of CCS technologies foster innovation in carbon management and related fields, advancing carbon capture and utilization methods.
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations: CCS provides a compliance solution to environmental regulations and carbon pricing, helping companies avoid fines and adapt to future standards.
- Supporting a Low-Carbon Economy: As the world moves towards a low-carbon economy, the advantages of Carbon Capture Storage become increasingly apparent.
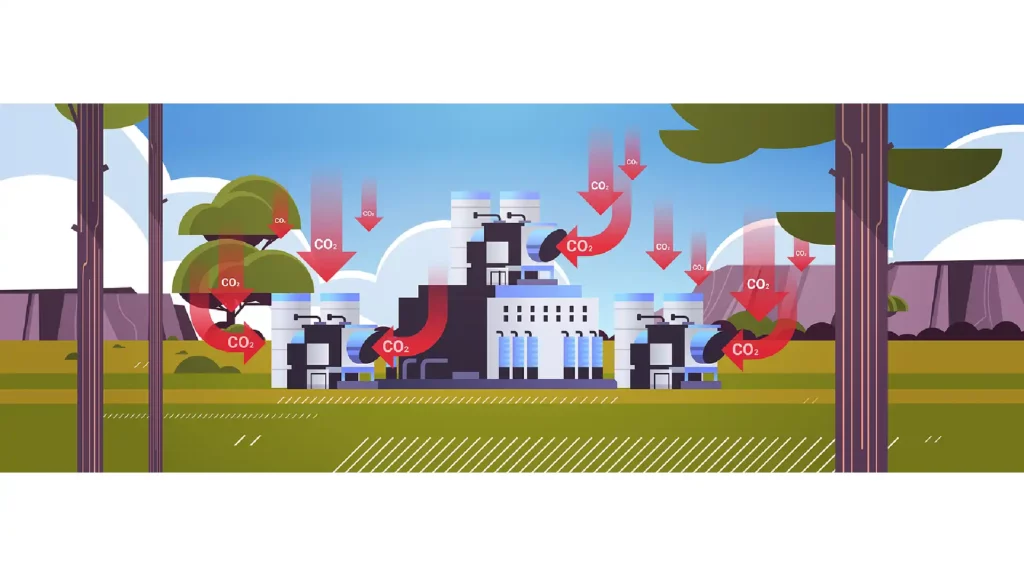

Advantages of Carbon Capture Storage on Global Impact and Policy Support
The global adoption of CCS is gaining momentum, thanks in part to supportive policies and international agreements aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Governments and international bodies recognize the advantages of Carbon Capture Storage, offering financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and research funding to accelerate its development and deployment.
- Strengthening International Collaboration for CCS Advancement
International collaboration is vital for the development and adoption of CCS solutions. It promotes the exchange of knowledge, technology, and best practices across countries.
This collaboration also helps in standardizing regulations and ensuring a unified global approach to carbon management.
Through joint research, investments, and policy-making, the international community is working towards a future where CCS technologies are widely used and integrated into the global energy and industrial sectors.
- Addressing Energy Security with CCS
One of the standout advantages of Carbon Capture Storage is its ability to bolster energy security, especially in regions with a heavy reliance on fossil fuels.
CCS aids countries in the clean usage of coal and gas, improving energy security and cutting carbon emissions. This helps maintain current energy infrastructure and resources while striving for environmental goals.
CCS is crucial for diverse energy strategies, allowing us to use fossil fuels responsibly while still combating climate change. It helps developing economies maintain energy independence and promote economic growth and quality of life.

Pros and Cons of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a pivotal technology in the fight against climate change, offering a path to significantly reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial sources and fossil fuel power generation.
However, like any technological solution, it comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Here, we explore the cons and pros of carbon capture and storage to provide a balanced view of its potential and limitations.
Pros of Carbon Capture and Storage
- Significant CO2 Emissions Reduction: CCS can capture up to 90% of CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial processes, making a substantial impact on reducing global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: It offers a way to continue using fossil fuel-based infrastructure with less environmental impact, easing the transition to renewable energy sources.
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): The use of captured CO2 for enhancing oil recovery not only improves the efficiency of oil production but also provides a potential revenue stream to offset CCS costs.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: Implementing CCS technology can lead to the creation of jobs across multiple sectors, including construction, engineering, and maintenance, contributing to economic development.
- Aids in Meeting Climate Targets: CCS is instrumental in helping countries achieve their greenhouse gas reduction commitments under international agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Flexible Application Across Industries: It can be applied to a variety of sectors, including power generation, manufacturing, and chemical processing, showing its versatility in addressing emissions from multiple sources.
- Supports Continuous Use of Coal and Natural Gas: CCS allows for the cleaner use of coal and natural gas, providing a pragmatic solution while renewable energy capacities are being scaled up.
Cons of Carbon Capture and Storage
- High Costs: The initial setup and operational costs of CCS are significant, including the expenses related to capture, transport, and storage of CO2.
- Energy Penalty: CCS processes consume a considerable amount of energy, which can decrease the overall efficiency of power plants and increase fossil fuel usage.
- Storage Risks: There are concerns about the potential for CO2 leakage from storage sites, which could undermine the benefits of CCS and pose environmental risks.
- Limited Storage Locations: The effectiveness of CCS is contingent upon the availability of suitable geological formations for CO2 storage, which are not uniformly distributed globally.
- Resource Allocation: Investing in CCS might divert attention and resources from renewable energy projects and technologies that are essential for a long-term sustainable energy transition.
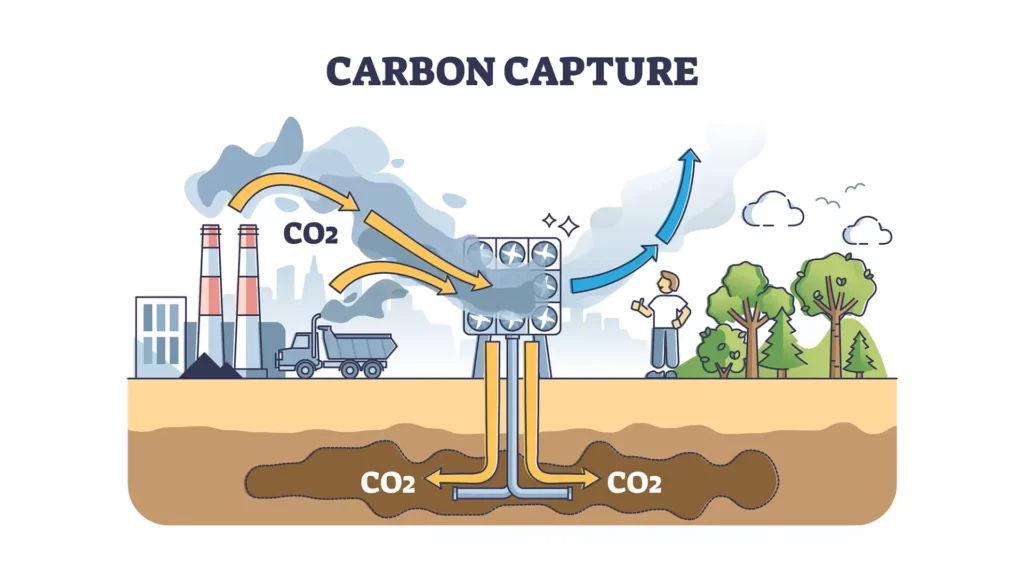
Career Opportunities in Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is vital for the environment and creates jobs. As we tackle climate change, the need for skilled workers in CCS is rising.
Carbon capture and storage jobs are vital in advancing CCS technologies and integrating them into energy and industrial systems. These roles include research, engineering, project management, policy analysis, regulatory compliance, and environmental monitoring.
As such, carbon capture and storage jobs offer a dynamic career path for individuals passionate about making a tangible impact on the world's environmental health while working at the forefront of technological innovation.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from sources like power plants and industrial processes, transports it to a storage site, and securely stores it underground in geological formations to prevent it from entering the atmosphere.
How does CCS help combat climate change?
CCS helps combat climate change by capturing CO2 emissions at their source and storing them away from the atmosphere, thereby reducing the amount of greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and climate change.
Is CCS technology currently being used?
Yes, CCS technology is currently being used in several countries around the world. There are multiple operational CCS projects in industries such as power generation, natural gas processing, and chemical production, with many more in various stages of development.
What are the main components of a CCS system?
The main components of a CCS system include:
- Capture: The separation and capture of CO2 from other gases produced at industrial and energy-related sources.
- Transport: The transportation of the captured CO2, usually via pipelines, to a storage location.
- Storage: The injection and permanent storage of CO2 into underground geological formations.
Can CCS be applied to any industrial facility?
While CCS can be applied to a wide range of industrial facilities, its feasibility and cost-effectiveness depend on several factors, including the facility's size, the concentration of CO2 in its emissions, proximity to storage sites, and the regulatory environment.
What are the Advantages of Carbon Capture and Storage?
When exploring the question, “What are the advantages of carbon capture and storage?” it becomes clear that this technology offers substantial benefits in the global effort to combat climate change. The advantages of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) lie primarily in its ability to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industrial and energy-related sources, directly addressing the urgent need to mitigate global warming.
How much CO2 can CCS capture?
The efficiency of CCS technologies can vary, but many current systems are capable of capturing 85% to 95% of the CO2 emissions from the source.
What are the benefits of carbon capture and storage?
When exploring the question, “What are the benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage?” it's essential to recognize the multifaceted advantages this technology brings to environmental conservation and the broader fight against climate change. The benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage are twofold, directly impacting both our planet's health and the sustainability of industries.
Can CCS create economic opportunities?
Yes, the development and implementation of CCS technology can create a wide range of economic opportunities, including job creation in engineering, construction, operation, and maintenance of CCS facilities, as well as in CO2 transportation and storage.
How does CCS fit into the broader climate change mitigation strategy?
CCS is one of several tools available to mitigate climate change. It complements other strategies such as the adoption of renewable energy, energy efficiency improvements, and conservation efforts, forming an integrated approach to reducing global greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages of Carbon Capture Storage Conclusion
The carbon capture and storage advantages are manifold, offering a viable solution to the pressing issue of climate change. From its environmental benefits and economic potential to technological innovations and global impact, CCS is a critical tool in our arsenal against global warming.
As we continue to refine and expand this technology, its role in shaping a sustainable future cannot be overstated.
In summary, the carbon capture and storage advantages underscore its importance in the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable world. By embracing CCS, we can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change, foster economic growth, and pave the way for a future where energy production aligns with environmental stewardship.