Alternative Energy – The Pros and Cons of Wind Turbines
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) met in Paris in 2015 to develop a global framework for greenhouse gas mitigation and alternative energy financing. The Paris Agreement was adopted on December 12, 2015, and opened for signatures at UN Headquarters on Earth Day, April 22, 2016.
Some countries have been noted for their leadership in alternative energy development, including Denmark, which produces and sells 140% of its electricity. Other countries have followed suit, and some are even exporting surplus electricity to neighboring countries.
The Power of Wind Energy
Wind energy is derived from the Earth's natural processes, primarily driven by the sun's uneven heating of the Earth's surface. As air heats up, it rises and creates areas of low pressure. Cooler air rushes in to fill these areas, creating wind. Wind turbines tap into this kinetic energy by capturing the movement of air and converting it into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy by the generator.
Renewable energy sources

There are numerous renewable energy sources available today. Wind, sun, water, biomass, and geothermal energy are all examples.
Each can be used for a variety of purposes, from cooking to lighting. The cost of solar power has been falling, but more affordable panels can now power entire neighborhoods.
But how do these sources compare to the fossil fuels we use today? This article will examine each of them in detail. The pros and cons of each can be clearly seen.
While renewables are abundant, they may not be economical for all applications. Solar photovoltaic systems, for example, produce electricity without a need for steam-generating equipment. In order to meet demand, renewable energy sources must be applied to large-scale electricity storage systems.
Renewables are an essential part of the global energy mix, but they require more infrastructure than traditional power sources. And it is important to remember that many renewable energy sources can be subsidized.
Inexhaustible, green, and renewable energy resources are vital to energy transition and global warming. These sources do not produce pollution and are naturally replenished. These energy sources help combat global warming and promote economic viability.
To make the transition to renewable energy sources more sustainable, we need to promote them. Listed below are five types of renewable energy sources. Hydroelectric power: This is a good alternative energy source that utilizes large areas of water to generate electricity.
The water movement in these locations causes the turbines and generators to spin, resulting in more energy being produced.
Renewable natural gas
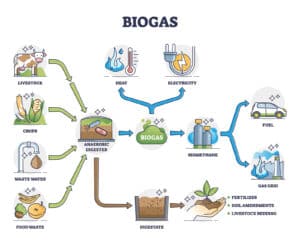
Using renewable natural gas as an alternative energy source is a viable way to complement current energy sources like composting, animal feed, and soil fertilizers. However, renewable natural gas projects are also more expensive than traditional energy sources and do not necessarily contribute to climate goals.
This WRI paper outlines common approaches, evaluation metrics, and considerations for renewable natural gas projects. Read on to learn more.
In this paper, we look at the pros and cons of renewable natural gas as an alternative energy source.
Although renewable natural gas is an acceptable alternative energy source, its use may distract from other critical decarbonization strategies. Renewable natural gas derived from waste has the potential to displace as much as four to seven percent of current natural gas consumption in the United States.
Additionally, biomethane can also provide waste management benefits. This means renewable natural gas could be an effective alternative energy source, while still posing a significant climate risk.
Biogas has been around for decades, but in the U.S., we're lagging behind Europe. The European continent alone contains over seventeen thousand biogas plants and more than two-thirds of the world's biogas electricity capacity.
The country of Denmark, for example, has over 160 biogas systems, and with a population of five million people, renewable natural gas provided 18 percent of the country's summer gas needs. Danish bioenergy firms estimate that renewable natural gas will replace fossil-derived natural gas in 20 years.
Wood

While burning wood for electricity releases less energy than burning fossil fuels, it does release a significant amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The forests take years to recover from the emissions and absorb pollution while growing.
This means that wood energy is not a good choice for developing countries where the climate is already warming up and oil and gas supplies are becoming scarce. However, in some places, alternative energy with wood is already a viable option. Read on to learn about the benefits of using wood for energy.
Woody biomass has been used by people for centuries to cook food, heat homes, and produce steam. As new technology has been developed, clean ways to harness wood's energy have been developed.
Today, woody biomass is a local renewable energy resource that can be easily obtained and produced. This article will look at two of the main types of wood biomass. Woody biomass can also be harvested from power lines and storms.
It can be used to generate electricity for heating homes and businesses.
Biomass energy can be produced from many different sources, including agricultural residues, lumber mill sawdust, and municipal and industrial waste. Agricultural residues, such as manure and sugar, can also be used as fuel.
In addition to biomass, methane can be produced from landfill fumes. Agricultural crop residues can be used to create alcohol. All of these products can be used to power generators or heat homes.
Wind
There are two main types of wind turbines: vertical and horizontal. Horizontal axis turbines have long, thin blades that resemble airplane propellers. Vertical axis turbines have shorter, wider blades, similar to those used in electric mixers.
The difference between these two types is the amount of wind power they can produce. The higher the wind speed, the more power each turbine can produce. Horizontal-axis turbines are typically more expensive and require more land space than vertical-axis turbines.
While both types of wind power have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, there are many similarities between them. In theory, wind power can generate up to 20 percent of the world's electricity. The problem is that the amount of energy it can produce is different in different locations.
For example, if you live in the Midwest, you might generate 20 percent more power than the next town over. Nevertheless, the costs of wind power are comparable to other types of energy.
In addition to the high price of wind power, it is not reliable. While it is not available in all places, it does produce intermittent power. It requires some system reserve capacity to compensate for the variability of wind generation.
Wind power can't be used by itself, so the grid needs to be designed to support this variable energy source. The best option for your power needs is to combine wind energy with conventional hydroelectricity. The two energy sources complement each other well.
How Wind Turbines Work
The Basic Mechanics
Wind turbines are sophisticated machines designed to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. They consist of several key components: the rotor, the generator, the tower, and the control system.
- Rotor: The rotor, often referred to as the blades, captures the energy from the wind. The design and number of blades can vary, affecting the efficiency of the turbine. The rotor is connected to the main shaft, which transfers the captured energy.
- Generator: The main shaft connects to a generator, which converts the rotational energy into electricity. This electricity is then either used directly or fed into the power grid.
- Tower: Wind turbines are mounted on tall towers to reach higher altitudes where wind speeds are stronger and more consistent. The tower provides stability and elevation to maximize energy capture.
- Control System: Modern wind turbines are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor wind direction and speed. These systems adjust the orientation of the blades to optimize energy capture and protect the turbine during high winds.
The Pros and Cons of Wind Turbines
The Pros of Wind Turbines
- Clean and Renewable Energy Source with Environmental Benefits: Wind turbines stand out as a remarkable source of electricity, harnessing wind's kinetic energy to generate power without releasing harmful greenhouse gases or pollutants into the atmosphere. This innovative technology aligns perfectly with the urgency to combat climate change and preserve air quality. Notably, wind energy diverges from conventional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, tapping into an infinitely renewable resource, thus establishing wind power as an environmentally friendly and sustainable option.
- Mitigation of Carbon Footprint with Implications for Climate Change: Wind energy exhibits a pivotal role in mitigating our carbon footprint by replacing conventional fossil fuel-based electricity generation. This substitution significantly diminishes the emission of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which is a major contributor to climate change and air pollution. By adopting wind energy on a broader scale, societies can proactively contribute to global efforts in curbing climate change while embracing a cleaner energy future.
- Economical Operation and Maintenance Dynamics: Following their installation, wind turbines present a remarkable advantage with their comparatively low operating costs. This characteristic stems from the technology's intrinsic design, which minimizes the need for extensive maintenance when contrasted with the ongoing expenses tied to traditional fossil fuel power plants. The economic viability of wind energy is further enhanced by the prolonged periods during which these turbines can effectively generate power.
- Catalyzing Job Creation and Local Economic Growth: The wind energy sector functions as an economic catalyst by creating jobs across a multifaceted spectrum. From manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research, a diverse array of employment opportunities arises, fostering growth within local economies. As this sector continues to expand, its impact on job creation becomes increasingly significant, amplifying the benefits of wind energy adoption.
- Versatility in Application for Diverse Settings: The versatility of wind turbines is a distinguishing characteristic, allowing them to be deployed across a wide array of settings. From expansive wind farms spanning vast landscapes to more compact residential installations, wind energy exhibits flexibility that transcends geographical boundaries. This adaptability empowers both urban and rural areas to harness the potential of wind energy, thus democratizing access to clean power.
- Reinforcing Energy Independence for Enhanced Security: By harnessing the power of wind, nations can effectively diminish their reliance on imported fossil fuels. This heightened energy independence contributes to national security and stability, as it mitigates vulnerability to fluctuations in global energy markets and geopolitical tensions surrounding resource access.
- Ensuring Long-Term and Sustained Energy Supply: The sustainability of wind energy is underscored by its foundation in an abundant and inexhaustible resource: the wind itself. Unlike finite fossil fuel reserves, wind remains an enduring source of energy, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply for generations to come. This perpetuity solidifies wind energy's role as a linchpin in the transition to a sustainable energy landscape.
The Cons of Wind Turbines
- Intermittency Challenges Demand Backup Solutions: One of the primary challenges associated with wind energy lies in its inherent intermittency, contingent upon the availability and strength of wind currents. This variability necessitates the implementation of backup power sources or sophisticated energy storage solutions to ensure an uninterrupted and reliable energy supply, particularly during periods of low wind activity.
- Navigating Visual and Auditory Concerns in Local Communities: Large-scale wind farms, while a beacon of renewable energy, can transform the visual landscape of local communities. The imposing structures of wind turbines, along with their rotational movement, can give rise to visual and noise impacts that influence the aesthetics of the environment. This can prompt concerns within communities, potentially affecting the level of public acceptance and support for wind energy projects.
- Ecological Impacts: Aerial Fauna and Wind Turbine Collisions The proliferation of wind turbines introduces a potential challenge to the welfare of aerial fauna, notably birds and bats. The rapidly spinning blades can pose a hazard, leading to collisions that may result in ecological disturbances and population declines for certain bird species. Balancing the benefits of wind energy with the preservation of biodiversity requires careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
- Land Use Dynamics and Ecological Disruption: Wind turbine installations necessitate considerable space, potentially conflicting with existing land uses and ecosystems. This could disrupt local habitats and landscapes, underscoring the need for meticulous site selection processes and comprehensive environmental impact assessments. These measures are essential to minimize the potential negative consequences of land use change associated with wind energy development.
Offshore wind

Offshore wind as an alternative energy source is a growing trend across the world. The United Kingdom leads the way, with more than ten gigawatts of installed capacity.
China and Germany are rapidly catching up, and by 2022, China's installed capacity will be larger than the UK and Germany combined.
The UK's commitment to renewable energy has helped the industry grow in the UK. The North Sea is the perfect location for offshore wind farms, and the UK government is considering ways to harness its abundance.
Offshore wind projects can provide massive amounts of renewable energy to load centers. Massachusetts has committed to generating nine gigawatts of offshore wind by 2035, which is the equivalent of 30 percent of the state's electricity needs.
Currently, the state has five projects under contract with total capacities of 4.3 gigawatts. Republican Gov. Charlie Baker has announced plans to create a $750 million clean energy investment fund to promote offshore wind projects.
This fund will aim to reduce strict price caps on electricity projects.
Federal investments in offshore wind should focus on creating a domestic supply chain. To ensure that offshore wind projects are profitable, the federal government should invest in helping states build regional economic hubs for the industry.
Investing in a national offshore wind supply chain is vital to achieving the goals of both renewable energy and climate action. And, if it works, the Biden administration should be proud of its efforts. It is clear that offshore wind is the future of energy, and it can boost the economy and create jobs for millions.
Conclusion
As the world grapples with the urgent need to transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, wind turbines stand tall as beacons of hope on the horizon. The journey to a greener future, however, is not without its twists and turns. Exploring the diverse facets of wind energy unveils a tapestry of benefits and challenges, each thread contributing to the complex fabric of our energy landscape.
The march towards a cleaner planet gains momentum with every gust of wind that turns the blades of a turbine. The promise of wind energy's potential to curb carbon emissions, create jobs, and bolster energy independence has sparked a global movement towards adoption. Nations that have embraced wind energy's embrace are leading the charge towards a future where pollution levels decline, and blue skies become a common sight.
Sources:
https://www.energyinformative.org/solar-energy-pros-and-cons/
https://www.ibtimes.sg/offshore-wind-power-key-achieving-renewable-energy–government-investment36165
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/the-role-of-federal-investment-in-offshore-winds-future
https://www.eei.org/issuesandpolicy/renewableenergy/Documents/Summary_OffshoreWind.pdf

