Biomass energy, a renewable energy source derived from organic materials, plays a pivotal role in Canada's energy portfolio.
As the world shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, understanding the significance, applications, and potential of biomass energy in Canada becomes crucial.
This guide delves deep into the subject, offering insights into how Canada is harnessing the power of biomass to fuel its future sustainably.
What is Biomass Energy?
Biomass energy refers to the energy produced from organic materials, such as plant matter and animal waste. This form of energy is renewable, as it utilizes resources that can be replenished over time, unlike fossil fuels.
The process of converting biomass into energy can take various forms, including combustion, gasification, and fermentation, each serving different energy needs.
The Role of Biomass Energy in Canada's Energy Landscape
Canada, with its vast forests and agricultural lands, holds significant potential for biomass energy production. Biomass energy in Canada contributes to the national energy mix by providing a cleaner, renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
It supports the country's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and plays a vital role in the transition towards a more sustainable energy future.

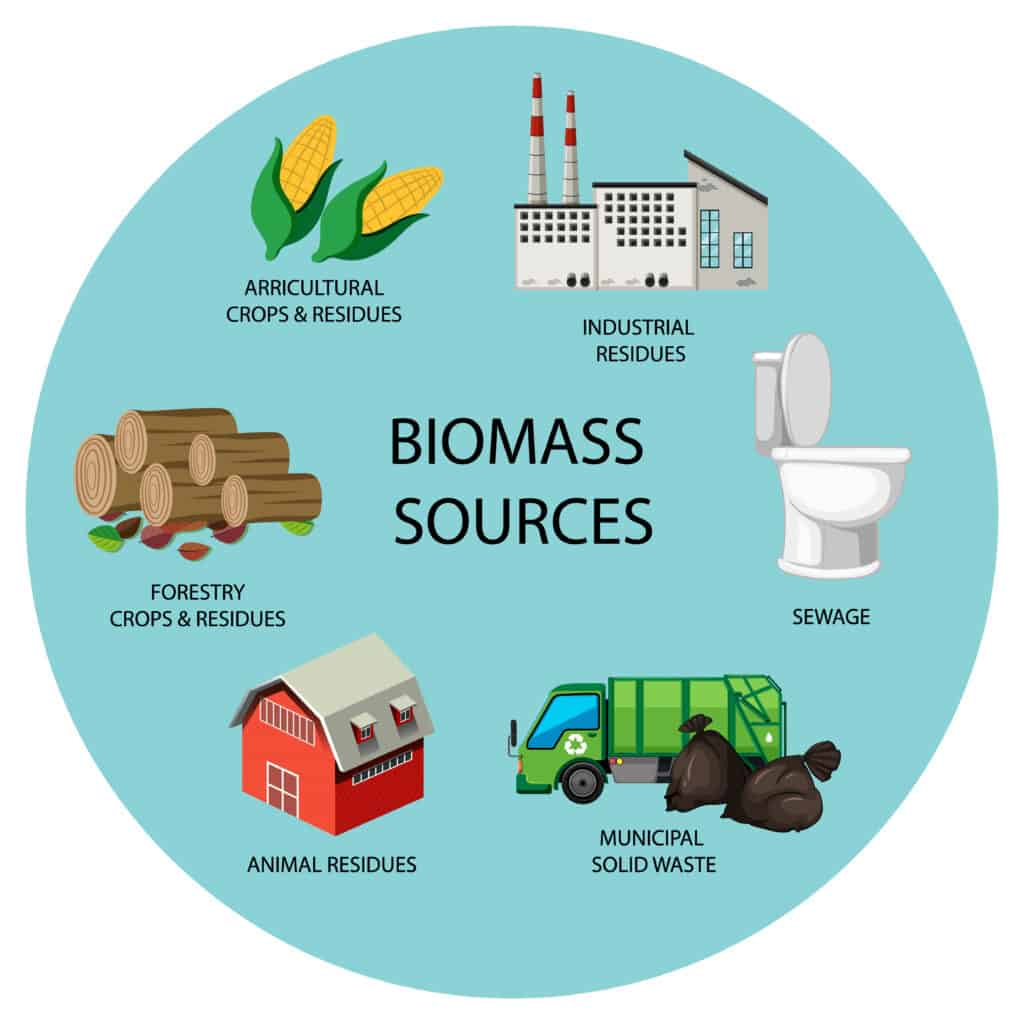
The Sources of Biomass Energy in Canada
Biomass energy, derived from organic materials, is key in Canada's energy landscape. Canada uses various biomass energy sources to generate energy, reducing emissions and creating jobs. The primary sources fueling the biomass energy sector in Canada are diverse and beneficial.
- Forestry Residues
Canada's biomass energy relies heavily on its forestry sector, a global leader in forestry. The country generates a large amount of residual materials like branches, bark, and sawdust from logging, along with wood chips from sawmills. These residues are a key source of sustainable biomass energy, used for electricity, heat, and biofuels.
- Agricultural Residues
Agriculture in Canada plays a key role in producing biomass energy. Residues from crops like straw, husks, and fruit leftovers, as well as livestock manure, are transformed into renewable energy through processes like anaerobic digestion.
This helps manage waste, reduces methane emissions, and provides energy for various purposes.
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
In Canada, municipal solid waste is now being used as biomass energy through technologies like anaerobic digestion and direct combustion.
This process converts organic waste into bioenergy, producing electricity, heat, and biogas. It helps reduce landfill waste and promotes a circular economy by turning waste into a valuable resource.
- Energy Crops
Dedicated energy crops like switchgrass, willow, and poplar are grown for biomass energy in Canada. They have high yield and energy content, often grown on marginal lands to avoid competition with food crops. These crops can be converted into biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel, offering a renewable option to fossil fuels.
- Expanding the Biomass Energy Portfolio
Canada is using various biomass sources like algae and industrial wastes to create high-energy biofuels.
This showcases Canada's innovative approach to renewable energy and commitment to a cleaner energy future.
The Benefits of Biomass Energy in Canada
Biomass energy in Canada offers numerous benefits, making it an attractive option for sustainable energy production. These benefits include:
- Renewability: Biomass energy comes from resources that can be replenished, ensuring a sustainable energy supply.
- Carbon Neutrality: Biomass energy can achieve near carbon-neutrality, as CO2 released during combustion is balanced by CO2 absorbed during plant growth.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing organic waste for energy production reduces landfill waste, aiding in effective waste management.
- Economic Development: The biomass sector creates jobs and supports economic growth, especially in rural areas with abundant biomass resources.
- Energy Security: Biomass energy enhances national energy security by reducing reliance on imported fuels and diversifying the energy mix.
- Versatility: Biomass can be converted into various energy forms (electricity, heat, biofuels), serving diverse energy needs.
- Support for Indigenous and Rural Communities: Biomass projects offer economic and energy opportunities for indigenous and rural communities, aligning with environmental values.

Tips for Maximizing the Potential of Biomass Energy in Canada:
- Invest in Research and Development: Focus on advancing biomass conversion technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Diversify Biomass Sources: Utilize a wide range of biomass materials, including agricultural waste, forestry residues, and municipal solid waste, to ensure a sustainable and reliable supply.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: Implement sustainable harvesting and cultivation practices to maintain the balance of ecosystems and ensure long-term biomass availability.
- Enhance Public Awareness: Increase awareness and understanding of biomass energy benefits among the public and stakeholders to foster acceptance and support.
- Strengthen Policy Support: Advocate for supportive policies, incentives, and funding from the government to accelerate the development and deployment of biomass energy technologies.
- Expand Infrastructure: Invest in the necessary infrastructure for biomass collection, transportation, and conversion to streamline the biomass energy supply chain.
- Foster Partnerships: Collaborate with research institutions, industry, and international partners to share knowledge, innovations, and best practices in biomass energy.
- Optimize Energy Systems: Integrate biomass energy into existing energy systems in a way that maximizes efficiency and minimizes environmental impacts.

Biomass Energy Plants in Canada's Renewable Future
Biomass energy plants in Canada play a vital role in the country's renewable energy efforts by converting forestry waste, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste into clean energy.
Biomass energy plants in Canada use local resources to produce energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
This innovative approach highlights Canada's commitment to renewable energy and sustainable energy future. Supporting these plants will enhance energy security, boost rural economies, and advance environmental conservation efforts.
Innovations in Biomass Conversion Technologies
Canada's renewable energy sector is evolving with new biomass conversion technologies, boosting efficiency and sustainability.
This positions Canada as a global leader in renewable energy.
- Advanced Thermal Conversion Techniques: Enhancements in gasification and pyrolysis processes increase efficiency and environmental performance, enabling cleaner syngas production and improved bio-oil quality.
- Biochemical Conversion Breakthroughs: Innovations in anaerobic digestion and advanced fermentation techniques lead to more efficient conversion of organic waste and agricultural residues into biogas and bioethanol.
- Efficiency Boost through Co-Generation: The adoption and optimization of co-generation systems significantly enhance the overall energy efficiency of biomass power plants by capturing and utilizing the heat generated during biomass conversion.
- Impact of Nanotechnology: The development of nanocatalysts and nanomaterials achieves more efficient conversion rates, lowers energy requirements, and broadens the range of biomass materials that can be processed.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being applied to optimize biomass conversion processes, predict the yield of biofuels, and enhance the operational efficiency of biomass energy plants.
- Development of Hybrid Systems: Combining different biomass conversion technologies to create hybrid systems that can process a wider variety of biomass types and produce multiple energy outputs, such as heat, electricity, and liquid fuels, from a single feedstock.
- Enhanced Feedstock Pre-treatment Methods: New pre-treatment techniques, such as steam explosion, acid hydrolysis, and enzymatic treatment, are improving the bioavailability of biomass for energy conversion, leading to higher yields of biofuels and biogas.

The Future of Biomass Energy in Canada
Canada's biomass energy sector is thriving due to a focus on innovation, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.
Supported by abundant natural resources and robust renewable energy policies, biomass energy is poised for growth, providing solutions to energy, environmental, and economic issues.
- Advancements in Technology and Efficiency
Advancements in technology are crucial for the future of biomass energy in Canada. Gasification, pyrolysis, and anaerobic digestion technologies are improving energy yield from biomass.
Next-generation biofuels like algae-based fuels and advanced bioethanol offer higher energy densities and lower environmental impacts, making biomass a more competitive option in the renewable energy market.
- Investment in Research and Development
Canada invests in R&D to improve biomass energy production by addressing cost and logistical challenges. Government and private funding support efforts to streamline supply chains, lower costs, and enhance sustainability.
- Expanding Market Opportunities
The demand for biomass energy in Canada is growing due to increasing need for clean, renewable energy in electricity, heating, and transportation sectors.
Policy measures like carbon pricing and renewable energy mandates are further driving this expansion.
- Focus on Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Sustainability is key for the future of biomass energy in Canada, with a focus on aligning production with environmental goals. Efforts include maintaining biodiversity, protecting resources, and promoting sustainable land use.
Lifecycle carbon emissions are also being monitored to maximize carbon neutrality potential, supporting Canada's climate change strategy.
- Economic and Social Impacts
Biomass energy growth in Canada benefits rural and indigenous communities by creating jobs and providing sustainable energy sources, boosting economic growth and energy security.
- Policy Support and International Collaboration
Canadian government supporting renewable energy & carbon reduction drives future of biomass energy. International partnerships on research & sustainability standards position Canada as global leader in biomass sector.

FAQs on Biomass Energy in Canada
Q1: What is biomass energy?
A1: Biomass energy is renewable energy derived from organic materials, such as wood waste, agricultural crops, and organic waste. It involves converting these materials into electricity, heat, or biofuels through various processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Q2: Why is biomass energy considered renewable?
A2: Biomass energy is considered renewable because it uses organic materials that can be replenished naturally over time, such as plants and trees. The CO2 released during biomass energy production is also offset by the CO2 absorbed by these plants during their growth, contributing to a cycle that can theoretically maintain balance with the environment.
Q3: How significant is biomass energy in Canada's energy mix?
A3: Biomass energy plays a significant role in Canada's energy mix, especially in rural and remote areas. It is a key component of Canada's renewable energy strategy, helping to diversify the energy supply, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and support economic development in biomass-rich regions.
Q4: What types of biomass materials are used in Canada for energy?
A4: Canada utilizes a wide range of biomass materials for energy, including forestry residues (like sawdust and wood chips), agricultural residues (such as straw and manure), municipal solid waste, and dedicated energy crops (like willow and switchgrass).
Q5: Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass energy?
A5: While biomass energy is considered cleaner than fossil fuels, there are environmental concerns, such as the potential for deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and air pollution from combustion. However, sustainable biomass sourcing and advanced conversion technologies can mitigate many of these concerns.
Q6: What are the latest innovations in biomass conversion technologies in Canada?
A6: Canada is at the forefront of developing advanced biomass conversion technologies, including improved gasification and pyrolysis processes, advancements in anaerobic digestion, and the use of nanotechnology and biotechnology to enhance biofuel production efficiency and sustainability.
Q7: Can biomass energy contribute to Canada's climate change goals?
A7: Yes, biomass energy can significantly contribute to Canada's climate change goals by providing a renewable, lower-carbon alternative to fossil fuels. When sustainably sourced and efficiently converted, biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and supports a transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Q8: How does biomass energy support rural and indigenous communities in Canada?
A8: Biomass energy supports rural and indigenous communities by creating jobs, providing local energy sources, and offering economic opportunities through the sustainable management of forestry and agricultural resources. Biomass projects can contribute to community energy self-sufficiency and economic resilience.
Q9: What is the future outlook for biomass energy in Canada?
A9: The future outlook for biomass energy in Canada is positive, with continued investment in research, development, and infrastructure expected to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and expand the range of usable biomass materials. As Canada aims for a more sustainable and diversified energy portfolio, biomass energy is poised to play an increasingly important role.
Q10: How can individuals and businesses get involved in biomass energy production in Canada?
A10: Individuals and businesses can get involved in biomass energy production by investing in biomass projects, utilizing biomass heating systems, participating in community biomass programs, or exploring opportunities for biomass feedstock supply. Engagement with local and national renewable energy associations can also provide valuable information and connections in the biomass energy sector.
Biomass Energy in Canada Conclusion
Biomass energy in Canada represents a key component of the country's renewable energy strategy.
With its vast resources, Canada is well-positioned to capitalize on the benefits of biomass energy, contributing to environmental sustainability, economic development, and energy security.
As technology advances and awareness grows, biomass energy in Canada is set to become an even more vital part of the global shift towards renewable energy sources.

