In recent years, the global emphasis on mitigating climate change has escalated, pushing countries around the world to adopt innovative and effective strategies to reduce their carbon footprints.
Among these strategies, Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) has emerged as a critical technology, especially in countries with significant industrial output. China, as the world's largest emitter of carbon dioxide, has been at the forefront of implementing CCS technologies.
This comprehensive guide explores the state of Carbon Capture and Storage China, delving into its importance, current projects, challenges, and future prospects.
The Significance of Carbon Capture and Storage China
Carbon Capture and Storage China is not just a technological endeavor; it is an essential part of the country's broader strategy to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
With its vast coal reserves, China relies heavily on coal-fired power plants, making the adoption of CCS technologies crucial for reducing emissions without drastically altering its energy infrastructure.
Moreover, Carbon Capture and Storage China serves as a model for other developing nations, demonstrating how rapid industrialization and environmental stewardship can coexist. By investing in CCS, China is paving the way for a sustainable future, balancing economic growth with ecological responsibility.

Current State of Carbon Capture and Storage China
China's commitment to Carbon Capture and Storage is evident in its growing portfolio of CCS projects. These range from small-scale pilot programs to large, commercial-scale operations.
The country's approach is holistic, targeting not only power generation but also industrial processes such as steel production and cement manufacturing, which are significant sources of CO2 emissions.
One of the flagship Carbon Capture and Storage projects in China is the Sinopec Qilu Petrochemical CCS project, which captures CO2 from petrochemical processes and utilizes it for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Similarly, the Huaneng Clean Energy Research Institute is leading the way with its CCS project in Beijing, capturing carbon from coal-fired power plants.
Benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage China
The adoption and advancement of Carbon Capture and Storage China offer a wide array of benefits, transcending environmental, economic, and social domains.
These advantages are pivotal not only for China's sustainable development but also for global efforts in combating climate change. Below is a consolidated list of the multifaceted benefits of implementing CCS in China:
- Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: CCS significantly lowers CO2 emissions from industrial and energy sectors, aligning with global climate targets and mitigating the impact of fossil fuel usage.
- Improved Air Quality: By capturing pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, CCS contributes to cleaner air, benefiting public health and reducing the occurrence of smog and acid rain.
- Enhanced Energy Security: CCS enables the cleaner use of China's abundant coal reserves, ensuring energy security and independence while minimizing environmental impact.
- Job Creation: The development, deployment, and operation of CCS technologies create new jobs, stimulating economic growth and providing opportunities in engineering, construction, and maintenance.
- Industrial Competitiveness: Leadership in Carbon Capture and Storage Technology enhances the global competitiveness of Chinese industries, particularly in manufacturing and clean energy sectors.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: CCS projects often accompany efforts to improve industrial energy efficiency, reducing energy costs and emissions simultaneously.
- Health Improvements: The reduction of harmful pollutants leads to better air quality, which directly benefits public health and may lower healthcare costs associated with air pollution-related diseases.
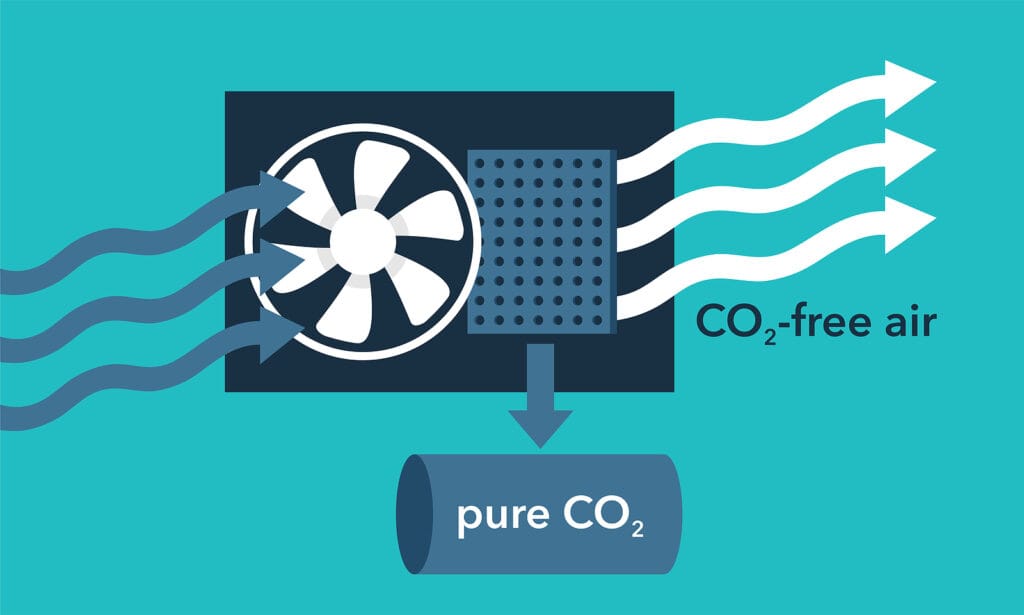

International Collaboration in Carbon Capture and Storage China Development
International partnerships have boosted China's CCS technology development, crucial for fighting climate change. Collaboration is key for advancing CCS projects in China and globally.
- Exchange of Knowledge and Expertise: International collaborations offer a platform for exchanging crucial knowledge and technical expertise related to CCS. This exchange includes best practices in capturing carbon dioxide, transportation logistics, storage solutions, and ways to enhance the overall efficiency and safety of CCS technologies.
- Technology Sharing and Development: Partnerships with leading CCS countries and organizations enable China to access cutting-edge technologies and innovative methodologies.
- Collaborations with the Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF): The CSLF is a key international initiative that brings together governments, private sectors, and non-governmental organizations to facilitate the development of CCS technologies worldwide.
- Engagement with the Global CCS Institute: The Global CCS Institute is an international think tank that works to accelerate the deployment of CCS globally.
- Bilateral Agreements with Leading CCS Countries: China has established several bilateral agreements with countries at the forefront of CCS technology, including the United States and Canada. These agreements facilitate focused collaboration on research and development projects, pilot programs, and technology exchanges.
- Participation in International CCS Research Initiatives: China is an active participant in various international CCS research and development initiatives. These initiatives provide platforms for collaborative research projects, which are essential for advancing CCS technologies and overcoming technical challenges through shared efforts.
- Addressing Global Climate Change Challenges Together: International collaboration in CCS development is not just about technological exchange; it's also a strategic alliance to combat global climate change. By working together, China and its international partners can leverage CCS technologies as a vital tool for reducing global carbon emissions, thereby contributing to the achievement of international climate goals.

Financing CCS Projects in China
Financing remains a critical factor in the deployment of Carbon Capture and Storage projects in China. Given the high initial costs associated with CCS technology, finding robust financing models is essential.
The Chinese government, along with private sector partners, is exploring various funding mechanisms, including green bonds, carbon trading revenues, and international climate funds.
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are also being considered as a viable option for funding large-scale CCS projects, ensuring their financial sustainability and success.
Enhanced Policies and Comprehensive Support for Carbon Capture and Storage China
China's government prioritizes Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) to achieve climate goals by implementing various supportive measures and policies.
The nation is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and embracing a sustainable energy future through financial, regulatory, and policy incentives for CCS technology growth.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies
The Chinese government offers financial subsidies to support CCS technology adoption, benefiting both public and private sectors. Tax incentives further boost investment by reducing costs and promoting economic viability.

Regulatory Support and Framework Enhancement
Regulatory support for CCS projects has been enhanced by clear guidelines and standards set by the government.
This helps mitigate risks and ensure smooth project implementation. Efforts to streamline approval processes are also underway to speed up CCS project development.
Strategic Integration into National Policy
China's latest Five-Year Plan highlights the significant support for Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in the country. The plan sets specific goals for CCS development, aiming to increase capacity by 2030 with targets for carbon capture, utilization, and storage.
This reflects China's commitment to CCS as a key strategy in addressing climate change and advancing towards a green economy.
Looking Forward: Continuous Support and International Collaboration
China is pushing forward with its CCS agenda, making policy adjustments to keep up with technology and market changes.
They are seeking international collaboration to improve CCS technologies through partnerships and research initiatives. This allows China to share and gain knowledge in CCS on a global scale.

The Future of Carbon Capture and Storage China
The future of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in China is poised for significant development, influenced by a combination of technological innovation, policy support, and international collaboration.
Below is an outline of key factors that will shape the trajectory of CCS in China:
- Technological Advancements: Continued research and development efforts are expected to lead to more efficient and cost-effective CCS technologies. This includes improvements in capture methods, reduction of energy consumption during the capture process, and innovative carbon utilization options.
- Policy and Regulatory Support: The Chinese government is likely to enhance its policy framework to provide clearer guidelines and stronger incentives for CCS projects.
- Expansion of Pilot Projects to Commercial Scale: Pilot projects currently in operation or in the planning stages are expected to transition to commercial-scale deployments.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: CCS technologies will increasingly be integrated with renewable energy sources. This integration aims to create a more flexible and sustainable energy system.
- International Cooperation: China is likely to strengthen its international partnerships in CCS research, development, and deployment. Collaboration with other countries and international organizations can facilitate knowledge exchange, co-investment in large-scale projects, and the development of global standards and best practices.
- Development of CO2 Utilization Technologies: The future of CCS in China includes not just storage but also the utilization of captured CO2 for various purposes, such as in enhanced oil recovery, the production of chemicals, and in building materials.
- Public Awareness and Acceptance: Efforts to increase public awareness and acceptance of CCS technologies will be crucial. Educating the public about the benefits and safety of CCS can help to mitigate concerns and foster community support for upcoming projects
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Carbon Capture and Storage in China
What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
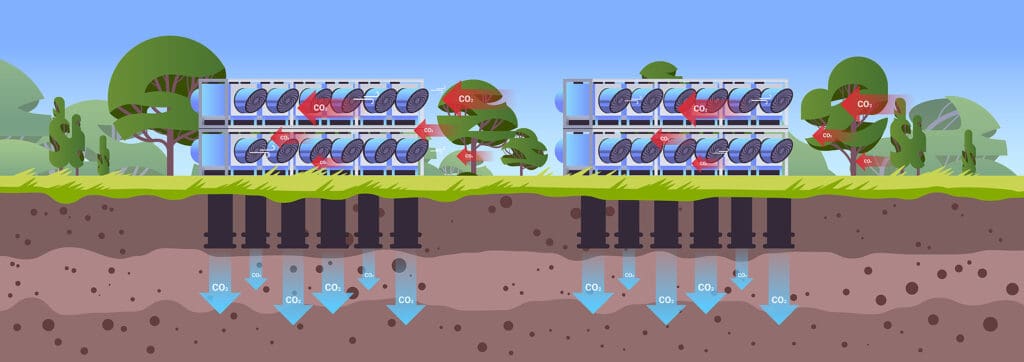
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology designed to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial sources and power generation. It involves capturing CO2 produced by these facilities before it is released into the atmosphere, transporting it to a storage site, and securely storing it underground in geological formations.
Why is CCS important for China?
CCS is crucial for China because it allows the country to reduce its CO2 emissions significantly while continuing to utilize its abundant coal resources for energy production. It plays a vital role in China's comprehensive strategy to combat climate change and meet its commitments under international agreements like the Paris Accord.
How does China's approach to CCS compare with other countries?
China's approach to CCS is proactive and comprehensive, focusing on both the energy sector and industrial processes. While many countries are exploring CCS, China is among the leaders in terms of the number and scale of projects underway. The government's strong support through policies and funding distinguishes China's efforts in the global CCS landscape.
What are the main applications of CCS technology in China?
In China, CCS technology is primarily applied in power generation, steel production, cement manufacturing, and petrochemical processes. These sectors are among the largest sources of CO2 emissions in the country, making them key targets for CCS projects.
How are CCS projects financed in China?
CCS projects in China are financed through a combination of government funding, subsidies, and investments from both state-owned and private enterprises. International collaboration and funding from environmental organizations also play a role in supporting CCS initiatives in China.
What are the challenges of implementing CCS in China?
The main challenges include high costs of capturing and storing CO2, technological barriers, the need for extensive infrastructure, and public acceptance of the technology. Additionally, developing a comprehensive regulatory framework for CO2 storage is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of CCS projects.
Is CCS safe?
Yes, when properly implemented, CCS is considered safe. The technology for capturing and storing CO2 is well-established, and there are strict regulations and monitoring protocols in place to ensure that CO2 remains securely stored underground. The risk of leakage is minimal, and ongoing research continues to enhance the safety and efficiency of CCS processes.
Can CCS help China achieve carbon neutrality?
CCS is one of the key technologies that can help China achieve its goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2060. By significantly reducing emissions from the largest industrial sectors and power generation, CCS complements other strategies like the expansion of renewable energy and energy efficiency improvements.
Are there any examples of successful CCS projects in China?
Yes, there are several examples of successful CCS projects in China, such as the Sinopec Qilu Petrochemical CCS project and the Huaneng Clean Energy Research Institute's CCS project in Beijing. These projects demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of CCS technology in reducing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power generation.
How can I learn more about CCS initiatives in China?
To learn more about CCS initiatives in China, you can consult publications from the International Energy Agency (IEA), research articles in academic journals, and reports from China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). These sources offer in-depth analyses and updates on the progress and development of CCS technology in China.
Carbon Capture and Storage China Conclusion
Carbon Capture and Storage China is at a critical juncture. As the country strides towards its ambitious climate targets, the role of CCS technologies cannot be overstated.
Despite facing challenges, the prospects for CCS in China are bright, driven by strong government support, technological advancements, and international cooperation.
As the world watches, China's journey with Carbon Capture and Storage could not only significantly reduce its carbon emissions but also serve as a beacon for other nations grappling with similar environmental challenges.
The success of Carbon Capture and Storage China will undoubtedly be a pivotal chapter in the global fight against climate change.

