Carbon Capture and Storage Technology
Discover the remarkable success of an anonymous power station, known as Project X, in revolutionizing sustainable energy. Through the implementation of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology, this visionary company has become a beacon of hope in the fight against climate change.
By capturing and storing CO2 emissions, Project X has significantly reduced its carbon footprint, positioning itself as a pioneer in the industry. This remarkable achievement serves as an inspiration for other companies striving to achieve carbon neutrality and embrace a sustainable future. Join the movement and unlock the transformative potential of CCS technology in creating a cleaner, greener world for generations to come.
Understanding Carbon Capture and Storage
Before we embark on the journey of Peterhead's success, it's crucial to understand what is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology entails.
CCS is a technique designed to help mitigate the greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change. The technology involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) at its source—usually large industrial plants or power stations—and subsequently storing it underground in geological formations.
The primary objective of CCS technology is to keep CO2, a potent greenhouse gas, out of the atmosphere. If successfully deployed at scale, CCS can help us transition to a low-carbon economy, thus combatting the adverse impacts of climate change.
History of Peterhead Power Station
Peterhead Power Station, located in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, has a unique story. Opened in 1982, it was initially powered by oil. However, in the mid-90s, it transitioned to using natural gas, a relatively cleaner fuel.
- Early Operations with Oil: When Peterhead Power Station first opened in 1982, it relied on oil as its primary fuel source. This reflected the prevailing energy landscape and the available technologies at that time.
- Transition to Natural Gas: In response to environmental concerns and evolving energy trends, Peterhead Power Station made a significant transition in the mid-1990s. It shifted from oil to natural gas as a cleaner and more sustainable fuel source. This transition aligned with the global shift towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
- Adoption of CCS Technology: In the early 2020s, Peterhead Power Station took a momentous step by embracing carbon capture and storage examples (CCS) technology. This decision showcased the power station's commitment to further reducing its carbon footprint and mitigating climate change impacts. It also demonstrated the station's dedication to embracing innovative solutions to address environmental challenges.
- A Milestone for the Energy Industry: The integration of CCS technology at Peterhead Power Station marked a significant milestone for the energy industry. It highlighted the station's role as a pioneer in adopting and implementing CCS on a large scale, serving as a model for other power stations and industries worldwide. This pivotal moment showcased the station's dedication to sustainability and its contribution to the transition towards a low-carbon future.
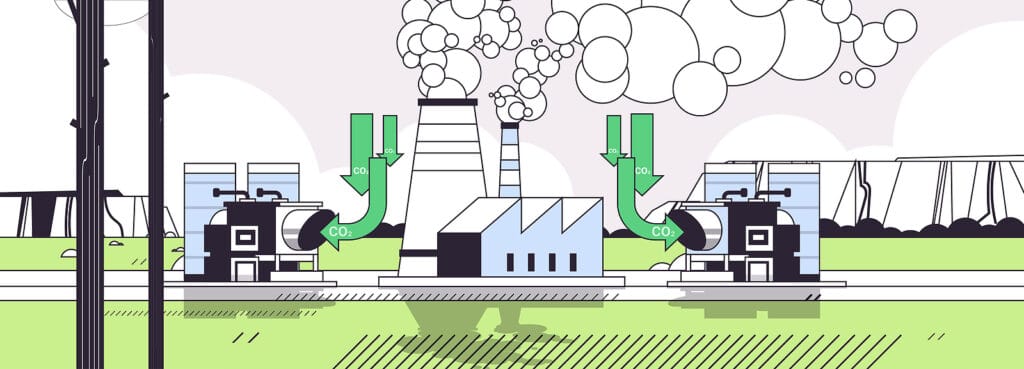
Implementing CCS Technology at Peterhead Power Station
The implementation of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology at Peterhead Power Station involved various stages and encountered significant challenges. Here is a detailed overview of the project:
- The Project Concept: The aim of the Peterhead CCS project was to capture a substantial portion (around 85-90%) of the CO2 emissions from one of the existing gas turbines at the power station. The captured CO2 would then undergo compression and be transported via existing pipelines to be stored safely beneath the North Sea.
- The Technical Process: Peterhead Power Station adopted a Post-combustion Capture system to capture CO2 emissions. This involved using a solvent to capture the CO2 from the exhaust gas of the gas turbine. The CO2-rich solvent would then undergo a process of heating to release the CO2 gas, which would be compressed and prepared for transportation and subsequent storage.
- The Challenges: The implementation of CCS technology at Peterhead Power Station posed several challenges, including:
- Adapting the existing infrastructure: Retrofitting the CCS system into an operating power station required modifications to the existing infrastructure, including the integration of new equipment and processes.
- Transportation of captured CO2: Establishing a reliable transportation system was crucial to ensure the safe and efficient delivery of the captured CO2 via existing pipelines to the storage site offshore.
- Secure storage locations: Identifying suitable and secure storage locations beneath the North Sea involved rigorous assessment of geological formations and ensuring long-term containment of the CO2.
- The Success Story: Despite the challenges faced, Peterhead Power Station emerged as a remarkable success story in the field of CCS technology. The power station accomplished its objective of capturing 85-90% of CO2 emissions, making it one of the largest power plants worldwide equipped with a full-chain CCS system.
- Validation of CCS technology: The successful implementation of CCS technology at Peterhead Power Station demonstrated the technical and commercial viability of large-scale carbon capture plant and storage.
- Setting a benchmark: Peterhead Power Station's success served as a benchmark for other power plants and industrial facilities globally, inspiring further adoption of CCS technology to mitigate CO2 emissions and combat climate change.
Impact on Climate Change
The success story of Peterhead Power Station has significant implications for climate change mitigation. The station's effective capture of CO2 emissions is a step toward achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
The Future of CCS Technology
The future of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology holds significant potential for addressing climate change. Here are some key factors that will shape its development:
- Regulatory Frameworks: To foster global adoption of CCS, governments around the world must establish supportive regulatory frameworks. This includes setting emission reduction targets, implementing policies that incentivize CCS deployment, and providing clear guidelines for CCS project development and operation.
- Financial Support: CCS projects require substantial investment due to the high costs associated with capturing, transporting, and storing CO2. Governments and international funding institutions need to provide financial support and incentives to encourage the deployment of CCS technology on a larger scale.
- Energy-efficient Capture Processes: Continuous research and development efforts should focus on enhancing capture technologies to improve their energy efficiency. Innovations like advanced solvents, membranes, and solid sorbents can help reduce the energy requirements for capturing CO2, making CCS more economically viable and environmentally sustainable.
- Sustainable Storage Sites: Identifying and utilizing suitable and sustainable storage sites for captured CO2 is essential. Research should be conducted to assess the geological suitability of potential storage sites, ensuring long-term stability and minimal environmental impact. Exploration of alternative storage options, such as carbon mineralization or utilization in industrial processes, can also contribute to the advancement of CCS technology.
- Monitoring and Verification Techniques: Robust monitoring and verification techniques are crucial to ensure the integrity and safety of stored CO2. Advances in monitoring technologies, such as satellite-based remote sensing and ground-based monitoring systems, can improve our ability to detect and measure stored CO2 and ensure its long-term containment.

The Economic Impact of Peterhead Power Station's CCS Project
In addition to job creation and local economic development, the successful implementation of CCS technology at the Peterhead Power Station has had several other economic impacts:
- Technology Development: The CCS project at Peterhead has contributed to the advancement of CCS technology. Through research, testing, and optimization, valuable knowledge and expertise have been gained, which can be applied to future CCS projects. This technological advancement can enhance the competitiveness of industries involved in CCS, driving innovation and fostering economic growth.
- Industry Growth: The establishment of the CCS project at Peterhead has created new opportunities for industries related to carbon capture and storage. Companies specializing in the development and deployment of CCS technologies, equipment manufacturing, engineering services, and consultancy have benefited from increased demand. This has the potential to attract investment and spur the growth of a robust CCS industry cluster, generating further economic activity and job opportunities.
- International Collaboration: The success of the Peterhead CCS project has positioned the region as a leader in CCS technology and expertise. This has opened doors for international collaboration, knowledge sharing, and partnerships. The region can benefit from the exchange of ideas, research collaborations, and the export of CCS-related services and technologies, creating additional economic opportunities.
- Environmental Compliance and Market Access: CCS technology enables industries to capture and store CO2 emissions, helping them meet emissions reduction targets and comply with environmental regulations. This enhances their social and environmental responsibility and can improve their access to international markets. By adopting CCS, industries in the region can maintain their competitiveness, attract investors, and access markets with stringent emission requirements, securing long-term economic viability.
Lessons from Peterhead for Future CCS Implementation
The success story of Peterhead Power Station offers valuable lessons for the future implementation of CCS technology. Understanding these lessons can help drive successful CCS projects elsewhere and bring us closer to a sustainable future.
- Technology Demonstration: The successful implementation of CCS at Peterhead Power Station serves as a critical technology demonstration for future CCS projects. It showcases the technical feasibility and effectiveness of CCS in reducing CO2 emissions from power generation. This demonstration provides valuable insights into the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of CCS facilities, helping to build confidence in the technology and encourage its adoption in other locations.
- Public Perception and Acceptance: The positive public perception and acceptance of the Peterhead CCS project highlight the importance of engaging with local communities and stakeholders from the early stages. By involving and informing the public about the benefits and safety of CCS technology, misconceptions and concerns can be addressed. This open and transparent communication fosters public trust and support, essential for the successful implementation of future CCS projects.
- Cost Reduction and Scalability: The experience gained from the Peterhead project provides valuable insights into cost reduction strategies and scalability of CCS technology. Lessons learned from optimizing the CCS process, enhancing efficiency, and minimizing operational costs can inform future projects and help drive down the overall cost of CCS implementation. These cost reductions are crucial for enabling wider adoption of CCS in various industries and achieving significant emissions reductions at a global scale.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: The success of the Peterhead CCS project highlights the importance of supportive policy and regulatory frameworks. Governments play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment for CCS implementation by providing clear regulations, financial incentives, and long-term policy commitments. By aligning policies and regulations with climate goals, governments can facilitate the deployment of CCS technology on a larger scale and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- International Cooperation: The Peterhead CCS project's international collaboration and knowledge sharing have been instrumental in advancing CCS deployment globally. Experience sharing, best practices, and joint research efforts among countries and organizations can accelerate the development and implementation of CCS technology worldwide. This collaboration can lead to further technological advancements, increased cost-effectiveness, and improved knowledge transfer, benefiting future CCS projects and fostering international cooperation in addressing climate change.
Conclusion
The Peterhead Power Station stands as a testament to the potential of carbon capture and storage technology in addressing climate change. While the journey has not been without challenges, the station's success demonstrates that with the right approach and relentless commitment, we can harness technology to create a sustainable future.
As the world grapples with the effects of climate change, the Peterhead Power Station success story inspires hope and sets the stage for the widespread implementation of CCS technology.
The story of the Peterhead Power Station is not just about a power station; it's about a global mission. A mission to mitigate climate change and safeguard our planet for future generations. And in this mission, Carbon Capture and Storage technology plays a pivotal role.
Sources
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/531393/11.063_-_Stakeholder_and_Public_E
- https://www.ssethermal.com/media/3isawytf/peterhe
- https://az659834.vo.msecnd.net/eventsairwesteuprod/production-ieaghg-public/34c434b4b9ad4650b5b28bae7edc5198
- https://www.lse.ac.uk/granthaminstitute/explainers/what-is-carbon-capture-and-storage-and-what-role-can-it-play-in-tackling-climate-change/

