Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
In the current era, where environmental sustainability has become a paramount concern, technologies such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) have emerged as key players in the fight against climate change.
This pivotal technology, aimed at reducing global carbon emissions, is not just a beacon of hope for a greener planet but also a burgeoning field for job creation.
In this guide, we delve deep into the realm of Carbon Capture Storage jobs, shedding light on the opportunities, challenges, and future prospects that this innovative field holds.
Introduction to Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
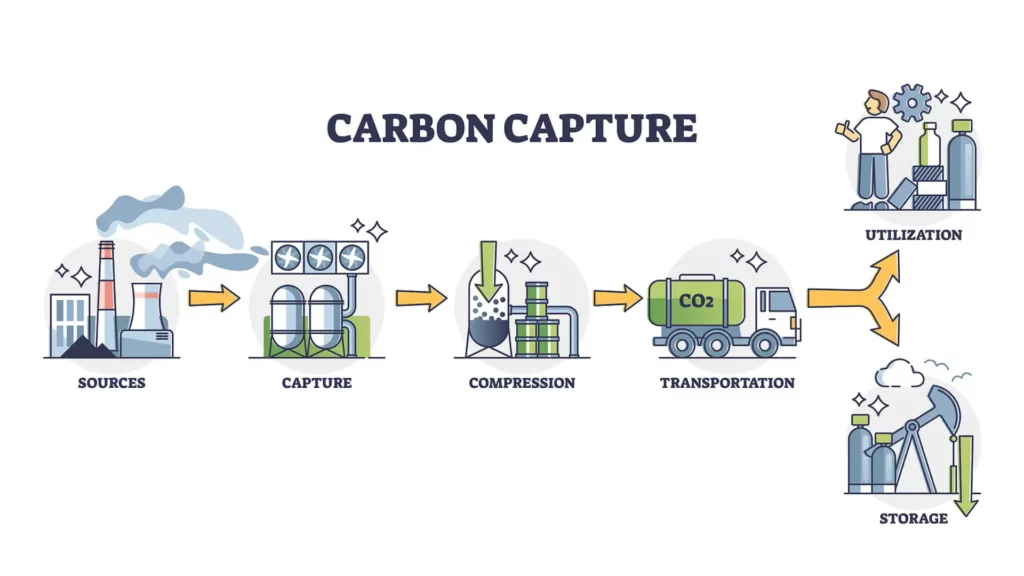
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology designed to capture carbon dioxide emissions from sources like coal-fired power plants, industrial processes, and even directly from the air, and store it underground in geological formations, thus preventing it from entering the atmosphere.
The significance of CCS technology in mitigating climate change cannot be overstated, making Carbon Capture Storage jobs critical in our collective efforts towards a sustainable future.

The Rising Demand for Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
As global awareness and legislative measures towards reducing carbon emissions intensify, the demand for professionals skilled in CCS technologies is on the rise.
Carbon Capture Storage jobs span a wide array of disciplines, from engineering and geology to policy analysis and project management.
This surge in demand underscores the importance of fostering a skilled workforce capable of advancing CCS technologies and implementing them on a scale necessary to achieve significant environmental impact.
Career Opportunities in Carbon Capture Storage
The CCS industry offers a diverse range of career paths, each playing a crucial role in the lifecycle of CCS projects:
- Research and Development: Innovators and scientists in R&D focus on advancing CCS technologies, making processes more efficient and cost-effective.
- Engineering and Design: Engineers play a pivotal role in designing and constructing CCS facilities, ensuring the safe and efficient capture and storage of carbon dioxide.
- Operations and Maintenance: Skilled technicians and operators are essential for the day-to-day running of CCS operations, ensuring systems function optimally.
- Regulatory Compliance and Policy: Experts in policy and legal frameworks guide CCS projects through the complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring compliance and securing permits.
- Environmental Monitoring and Risk Assessment: Specialists in environmental science ensure that CCS projects do not adversely affect surrounding ecosystems and assess risks associated with carbon storage.

Training and Education for a Career in CCS
To succeed in CCS careers, a strong foundation in specialized knowledge and skills is essential due to its interdisciplinary nature.
This guide explores educational requirements, certifications, and ongoing learning to excel in the field.
Academic Foundations: Degrees and Specializations
A strong academic background forms the cornerstone of a career in CCS. Prospective candidates are encouraged to pursue undergraduate and, if possible, advanced degrees in key disciplines that are integral to CCS operations:
- Environmental Science and Engineering: These programs provide a solid grounding in the principles of environmental conservation, pollution control, and the technological aspects of CCS.
- Chemical and Mechanical Engineering: Given that CCS involves the capture and transformation of carbon dioxide, degrees in chemical and mechanical engineering are highly relevant.
- Geology and Earth Sciences: Specializing in geology or earth sciences is particularly beneficial for those interested in the storage aspect of CCS.
- Energy Policy and Management: For individuals inclined towards the regulatory, policy, and management aspects of CCS, degrees in energy policy, environmental law, and project management are invaluable.

Professional Certifications and Specialized Training
Certifications and targeted training programs boost career growth in Carbon Capture Storage jobs by providing professionals with updated knowledge on CCS carbon capture and storage technologies, regulations, and industry best practices.
Key courses and certifications include:
- Certified Carbon Capture and Storage Professional: Offered by various professional bodies, this certification validates expertise in CCS technology, project implementation, and compliance with environmental standards.
- CCS Technology and Operations Certification: Focused on the technical and operational aspects of CCS, this certification covers the entire lifecycle of CCS projects, from design and capture to transportation and storage of carbon dioxide.
- Sustainable Energy Systems and Management Courses: These courses provide insights into integrating CCS within broader sustainable energy systems, emphasizing energy efficiency, renewable energy synergies, and carbon management strategies.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Professionals in Carbon Capture Storage must stay updated on technology, regulations, and industry trends through workshops, conferences, webinars, and professional organizations.
This commitment to ongoing learning and networking is essential for staying competitive in the field.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in CCS Careers
Technology and innovation drive the CCS industry by creating new methods to capture, transport, and store carbon dioxide.
These advancements are shaping CCS jobs and providing diverse opportunities for professionals. Explore the cutting-edge technologies shaping the future of CCS and the career landscape in this vital sector.
- Advanced Capture Technologies: Advancements in capture tech are vital for boosting efficiency and cutting costs of CCS. Methods like post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion are improving, as well as new absorbents, adsorbents, and membranes for better CO2 capture.
- Transportation Innovations: Transporting CO2 safely and efficiently is crucial for CCS scalability. New pipeline materials resistant to CO2 corrosion and improved shipping and rail tech are extending CCS project capabilities.
- Enhanced Storage Solutions: Reliable storage is crucial for CCS success. Research on mineralization could create stable minerals from CO2 for long-term storage.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC) Technologies: DAC technologies are at the forefront of CCS innovation, capturing CO2 directly from the atmosphere. These advancements could help reduce emissions and lower CO2 levels, impacting climate change mitigation.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Integrating CCS with renewables improves sustainability by addressing intermittency and using surplus energy to power operations, reducing carbon footprint and costs.
- Digitalization and Smart Technologies: Digital technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT improve efficiency, safety, and maintenance predictions in CCS operations. Smart monitoring and data analytics are essential for managing CCS facilities and maintaining CO2 storage integrity.
- Policy and Economic Modeling Tools: Policy and economic tools are crucial for evaluating CCS projects, aiding in market understanding, regulatory impact, and financial incentives for large-scale deployment of CCS technologies.
- Public Engagement and Education Technologies: Using VR and AR to educate people about CCS can increase support for projects by providing immersive experiences that explain the processes and benefits of CCS for fighting climate change.

Challenges Facing Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
Despite the promising outlook, the field of CCS faces several challenges:
- Technological Hurdles: Continuous innovation is required to improve efficiency and reduce costs associated with CCS technologies.
- Regulatory and Policy Uncertainties: The evolving nature of environmental regulations can impact project viability and job security in the CCS sector.
- Public Perception and Acceptance: Gaining public trust and understanding of CCS technologies is crucial for the widespread adoption and support of CCS initiatives.
The Future of Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
CCS jobs are growing rapidly due to the global push for combating climate change. Governments and the private sector are investing heavily in CCS technologies, highlighting their importance in meeting climate goals and creating new jobs.
- Escalating Global Investments in CCS
As awareness of the climate crisis rises, funding for CCS technology is increasing. This includes research, infrastructure expansion, and deploying CCS facilities on a large scale to address global environmental challenges.
- IEA's Endorsement and the Job Market Implications
The IEA's approval boosts confidence in CCS, highlighting its role in achieving net-zero emissions.
This is expected to create new jobs in engineering, technical, and policy-making fields to support CCS implementation.
- Technological Maturation and Economic Viability
Advancements in CCS tech are key for a sustainable future. As costs decrease and tech improves, more industries can adopt CCS, boosting job opportunities.
Economies of scale and tech progress will make CCS projects appealing for long-term investment and environmental benefits.
- The Expanding Scope of Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
The growing Carbon Capture Storage industry requires diverse professionals skilled in geoscience, engineering, law, and project management.
As projects increase worldwide, there will be a need for workers proficient in monitoring, maintenance, and regulatory compliance for safe CO2 sequestration.
evolution offers various opportunities for individuals interested in environmental sustainability.
- A Call to Action for Aspiring Professionals
The field of Carbon Capture Storage jobs provides a fulfilling career path for those passionate about protecting the planet's future. With the urgent need for innovative solutions to combat the climate crisis, working in CCS offers both personal growth and a chance to contribute to environmental preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Carbon Capture Storage Jobs
Q1: What qualifications do I need to work in Carbon Capture Storage?
A: Careers in Carbon Capture Storage typically require a background in environmental science, engineering (chemical, mechanical, environmental), geology, or a related field. Higher positions may require advanced degrees or specialized training in CCS technologies. Additionally, certifications related to environmental management or sustainability can be beneficial.
Q2: Are Carbon Capture Storage jobs in demand?
A: Yes, the demand for Carbon Capture Storage jobs is on the rise globally. As governments and corporations commit to reducing carbon emissions, the need for skilled professionals in CCS technologies continues to grow. This trend is expected to accelerate as more CCS projects are developed and implemented.
Q3: Can I transition to a Carbon Capture Storage job from a different industry?
A: Absolutely. Many skills are transferable to the CCS field, especially from sectors like energy, manufacturing, environmental consulting, and engineering. Professionals with experience in project management, regulatory compliance, and environmental science can also find opportunities. A focus on upskilling or reskilling through CCS-specific courses or certifications can facilitate this transition.
Q4: What is the average salary for Carbon Capture Storage jobs?
A: Salaries in the CCS field can vary widely depending on the job role, experience level, and geographical location. Engineering and managerial positions in CCS projects often command higher salaries, reflecting the specialized skills and experience required. Research and policy roles may have different pay scales but offer other forms of professional satisfaction and impact.
Q5: How can I stay updated on trends in Carbon Capture Storage technology and job opportunities?
A: Staying updated can be achieved by following industry news, participating in relevant professional associations, attending conferences, and networking with professionals in the field. Online platforms and forums dedicated to CCS and sustainability topics are also excellent resources for the latest developments and job postings.
Q6: What are the biggest challenges in pursuing a career in Carbon Capture Storage?
A: Challenges may include the need for specialized education and training, navigating the evolving landscape of environmental regulations, and the industry's competitive job market. Additionally, as CCS technologies and policies develop, professionals must be committed to continuous learning and adaptation.
Q7: How can I contribute to the CCS field outside of direct employment?
A: Contributions to the CCS field can come in many forms, including academic research, policy advocacy, community education, and volunteering with organizations focused on environmental sustainability. Engaging in public discourse on the importance of CCS technologies and supporting policies that facilitate CCS projects are also valuable ways to contribute.
Q8: Are there international opportunities in Carbon Capture Storage jobs?
A: Yes, CCS is a global industry, with projects and research initiatives taking place all over the world. Professionals may find opportunities in countries leading in CCS deployment, such as the United States, Canada, Norway, and Australia, among others. Language skills and familiarity with international regulations can be advantageous for those seeking careers abroad.
Carbon Capture Storage Jobs Conclusion
Carbon Capture Storage jobs represent a dynamic and evolving field with the potential to significantly contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
As the demand for these jobs grows, so does the need for a skilled workforce equipped with the knowledge and expertise to drive forward CCS technologies.
For those looking to make a difference in the world, a career in Carbon Capture Storage offers not just a job, but a mission – a chance to be at the forefront of the fight against climate change and to contribute to a sustainable future for all.

