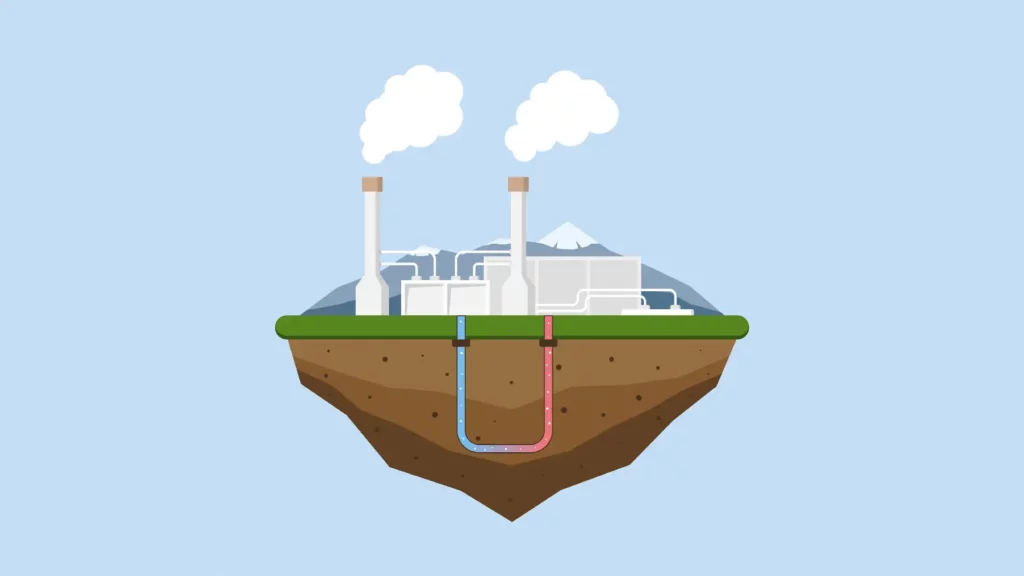
Geothermal energy is a clean and renewable source of power that harnesses the Earth's natural heat from within.
In Massachusetts, a state known for its commitment to environmental sustainability, geothermal energy is gaining momentum as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
In this guide, we will delve deep into the world of geothermal energy in Massachusetts, exploring its benefits, challenges, applications, and the initiatives driving its growth.
What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses the heat stored within the Earth's core to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling for buildings.
Unlike solar and wind energy, which rely on external factors, geothermal energy is available 24/7, making it a reliable and consistent source of power.
How Does Geothermal Energy Work?
To understand geothermal energy in Massachusetts, it's essential to grasp the basic principles of how it works:
Heat Extraction
Geothermal systems use heat pumps to extract heat from the Earth's subsurface, where temperatures are relatively stable year-round.
Heat Conversion
The extracted heat is converted into electricity or used directly for heating and cooling purposes.
Sustainability
Geothermal energy is sustainable, as it relies on the Earth's continuous heat production.

The Geothermal Potential in Massachusetts
- Geological Suitability
Massachusetts may not have the geothermal potential of some western states, but it still offers opportunities for geothermal energy development. The state's geology is characterized by sedimentary basins and fault systems, which can provide access to geothermal resources, especially in regions near fault lines.
- Temperature Gradient
The temperature gradient in Massachusetts varies depending on location and depth. While the state may not have extremely high geothermal temperatures, it is still possible to extract heat from the Earth's crust at depths reachable by drilling. Ground temperatures remain relatively stable year-round, making geothermal systems efficient for heating and cooling.
- Heat Pump Systems
Ground-Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) are a popular choice for geothermal heating and cooling in Massachusetts. These systems use the Earth's stable temperatures to exchange heat through a series of underground pipes, making them highly efficient and eco-friendly.

Benefits of Geothermal Energy in Massachusetts
The adoption of geothermal energy in Massachusetts offers a wide range of benefits, both environmental and economic:
- Renewable and Sustainable: Geothermal energy is an entirely renewable resource, as the Earth's heat is essentially inexhaustible on human timescales. Utilizing this energy source reduces Massachusetts' reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Energy Cost Savings: One of the most significant advantages of geothermal energy is its potential for cost savings. While initial installation costs can be relatively high, the long-term operational costs are significantly lower than those of traditional heating and cooling systems. In Massachusetts, where energy costs can be substantial, these savings can be especially beneficial for homeowners and businesses.
- Environmental Impact: Geothermal energy production has a minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. It produces very few emissions and significantly reduces a building's carbon footprint.
- Job Creation: The growth of the geothermal energy sector in Massachusetts has the potential to create numerous jobs, from geologists and engineers involved in project development to technicians responsible for system installation and maintenance.
- Energy Independence: By harnessing the Earth's heat, Massachusetts can reduce its dependence on external energy sources, providing greater energy security and stability for the state.
- Reduced Price Volatility: Geothermal energy's stable and consistent supply reduces vulnerability to price fluctuations in the fossil fuel market, ensuring more predictable and manageable energy costs for consumers.
- Enhanced Property Value: Homes and businesses equipped with geothermal systems often experience increased property values due to their energy efficiency and environmentally friendly features, making them more attractive to buyers and investors.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Geothermal energy diversifies Massachusetts' energy portfolio, making the state less reliant on any single energy source and increasing resilience in the face of energy supply disruptions.

Installation of Geothermal Energy in Massachusetts
The geothermal installation system is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution. Here's a detailed breakdown of each step:
Geological Assessment and Site Selection
A geological assessment is done before installation to check if the site is suitable.
Factors like soil composition, stability, and underground obstacles are considered. Site selection is important for efficient heat capture.
Borehole Drilling or Loop Installation
Once the site is selected, the next step involves drilling boreholes or installing horizontal loops. The choice between vertical boreholes and horizontal loops depends on the available space and geological conditions.
- Vertical Boreholes: In this method, vertical holes are drilled deep into the ground, typically ranging from 100 to 400 feet deep, depending on local geology. These boreholes are filled with a heat transfer fluid, such as a water and antifreeze mixture, which circulates to absorb heat from the surrounding earth.
- Horizontal Loops: When space constraints or geological conditions make vertical drilling impractical, horizontal loops are installed just below the surface. Trenches are dug to accommodate the loop piping, which is then buried.
Ground-Source Heat Pump or Geothermal Power Plant Installation
The choice between a ground-source heat pump system and a geothermal power plant depends on the intended application:
- Ground-Source Heat Pump: For residential and commercial buildings, ground-source heat pump systems are commonly used. These systems consist of a heat pump unit installed within the building and connected to the ground loop.
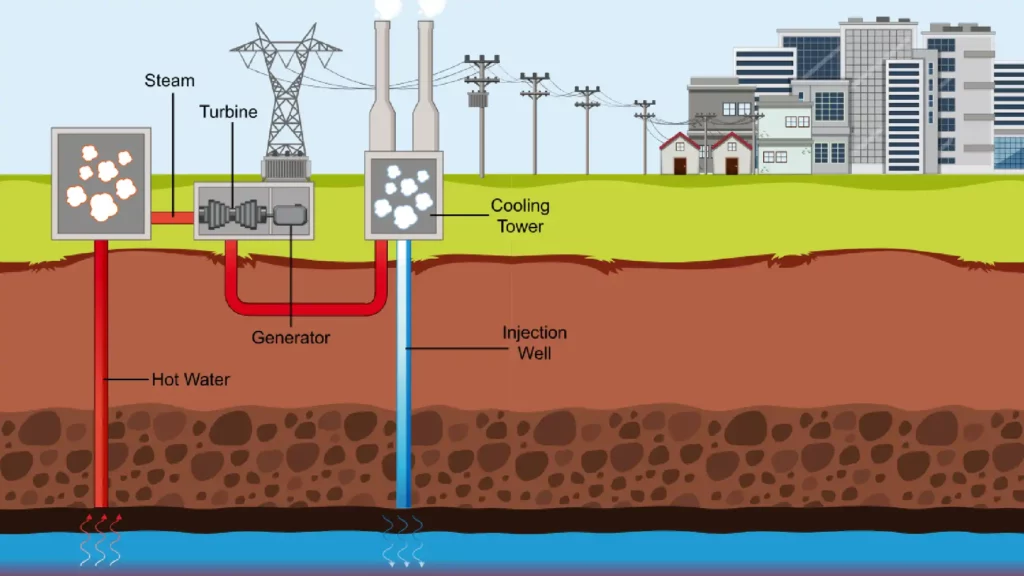
- Geothermal Power Plant: In larger-scale applications, such as power generation, geothermal power plants are employed. These plants tap into deeper reservoirs of hot water or dry steam beneath the Earth's surface.
Distribution Network Connection
After installation, the geothermal system must be connected to the building's HVAC network. This can be done by integrating it with the existing system or designing a new one to meet its needs.
- Radiant Floor Heating: Radiant floor heating systems are a popular choice for distributing geothermal heat. Tubes or pipes carrying heated fluid are embedded in the floor, providing even and efficient heating.
- Forced Air Systems: In some cases, geothermal systems can be integrated with forced air systems, allowing for both heating and cooling through ductwork.
Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the geothermal system. Maintenance tasks include:
- Fluid Inspection: Periodically check the heat transfer fluid for proper levels and quality to maintain efficient heat exchange.
- System Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the entire system, including the heat pump unit, loop piping, and distribution network, to identify and address any issues.
- Filter Replacement: Replacing air filters in the heat pump to maintain air quality and system efficiency.
- System Tuning: Fine-tuning the system settings to maximize energy efficiency and minimize energy consumption.
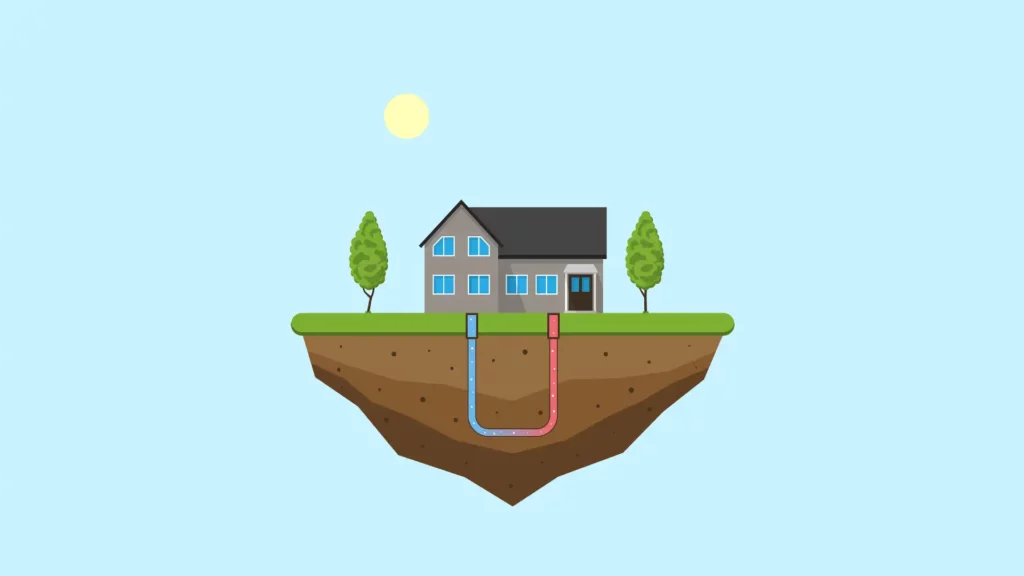

Environmental Impact of Geothermal Energy Massachusetts
Geothermal energy Massachusetts has a minimal environmental footprint compared to fossil fuels. The key environmental benefits include:
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Geothermal energy systems produce very low levels of greenhouse gases, making them a crucial tool in combating climate change.
Water Conservation
Geothermal power plants consume less water compared to conventional power plants, reducing stress on local water resources.
Land Use
Geothermal power plants occupy relatively small land areas, minimizing habitat disruption and land use conflicts.
Future Prospects and Potential Growth
The future of geothermal energy in Massachusetts looks promising, with the state committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and expanding its renewable energy portfolio. As technology advances and public awareness increases, we can expect to see:
Increased Adoption
As the benefits of geothermal energy massachusetts become more widely recognized, adoption rates are likely to rise, particularly in residential and commercial sectors.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development efforts are expected to lead to more efficient and cost-effective geothermal systems, further incentivizing adoption.
Policy Support
Continued government support, policy incentives, and streamlined regulations will play a crucial role in promoting geothermal energy Massachusetts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Geothermal Energy in Massachusetts
What is the current status of geothermal energy adoption in Massachusetts?
The adoption of geothermal energy in Massachusetts is steadily growing. The state has implemented various incentives and initiatives to promote geothermal projects, making it an attractive option for homeowners and businesses looking to transition to clean energy sources.
Are there any financial incentives for installing geothermal systems in Massachusetts?
Yes, Massachusetts offers financial incentives and tax credits to encourage the installation of geothermal heat pump systems. These incentives can significantly offset the initial costs of geothermal system installation.
How does geothermal energy compare to other renewable energy sources in Massachusetts?
Geothermal energy has its unique advantages, such as year-round heating and cooling capabilities, high energy efficiency, and minimal environmental impact. While solar and wind power are popular in Massachusetts, geothermal energy complements these sources by providing consistent energy generation.
What are the maintenance requirements for geothermal systems in Massachusetts?
Geothermal systems in Massachusetts require minimal maintenance compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. Regular check-ups and servicing by trained professionals can help ensure optimal performance.
Is geothermal energy suitable for all types of buildings in Massachusetts?
Geothermal systems can be installed in various types of buildings, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties. The feasibility of a geothermal system depends on factors like available land, geology, and heating and cooling needs.
How can I find a reliable geothermal system installer in Massachusetts?
You can find experienced and certified geothermal system installers in Massachusetts through online directories, local business listings, or by contacting organizations such as the Massachusetts Clean Energy Center (MassCEC) for recommendations.
Is geothermal energy environmentally friendly in Massachusetts?
Yes, geothermal energy is environmentally friendly in Massachusetts. It produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, reduces water consumption compared to conventional power plants, and has a smaller land footprint, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
What role does geothermal energy play in achieving Massachusetts' climate goals?
Geothermal energy plays a crucial role in Massachusetts' efforts to reduce carbon emissions and achieve its goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. By transitioning to geothermal systems, the state can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Can geothermal energy systems be integrated into existing heating and cooling systems in Massachusetts?
Yes, geothermal systems can often be integrated into existing heating and cooling systems, especially in retrofitting projects. It's essential to consult with a professional installer to determine the feasibility and best approach for integration.
What is the payback period for geothermal system installations in Massachusetts?
The payback period for geothermal system installations in Massachusetts varies depending on factors like system size, energy savings, and available incentives. On average, homeowners and businesses can expect to see a return on their investment within a few years, thanks to reduced energy bills and available incentives.
Geothermal Energy in Massachusetts Conclusion
Geothermal energy in Massachusetts is a clean, sustainable, and efficient solution for meeting the state's energy needs while reducing carbon emissions.
As awareness grows and technological advancements continue, the future of geothermal energy Massachusetts is indeed bright.
By harnessing the Earth's heat, the state is taking a significant step towards a greener and more sustainable energy future.
Source
https://www.energy.gov/eere/geothermal/articles/geothermal-technologies-program-fact-sheet