In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, India is turning its gaze towards one of its most abundant natural resources: water.
Hydro energy, also known as hydroelectric power, stands out as a pivotal element in India's energy portfolio, promising to play a crucial role in the nation's journey towards energy self-sufficiency and environmental sustainability.
This guide delves into the nuances of hydro energy India, exploring its potential, challenges, and future prospects.
Through a detailed exploration, we aim to provide an insightful resource for stakeholders and enthusiasts alike, keen on understanding and harnessing the power of hydro energy India.
What is Hydro Energy?
Hydro energy, also known as hydroelectric power, is electricity generated by harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water.
It's one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy, capitalizing on the water cycle that is naturally replenished by the sun, making it sustainable and reliable.
Hydroelectric power plants convert this kinetic energy into electricity through turbines and generators. There are primarily three types of hydroelectric facilities:
- Run-of-River: These plants generate electricity without significantly disrupting the natural flow of the river. They are typically smaller and have less environmental impact than other types of hydroelectric power plants.
- Reservoir (Dam): This type involves creating a large reservoir behind a dam. Water released from the reservoir flows through turbines, generating electricity. These plants can store energy and generate power on demand, making them more flexible.
- Pumped Storage: These facilities store energy by pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir during periods of low demand. When demand is high, water is released back into the lower reservoir through turbines, generating electricity.
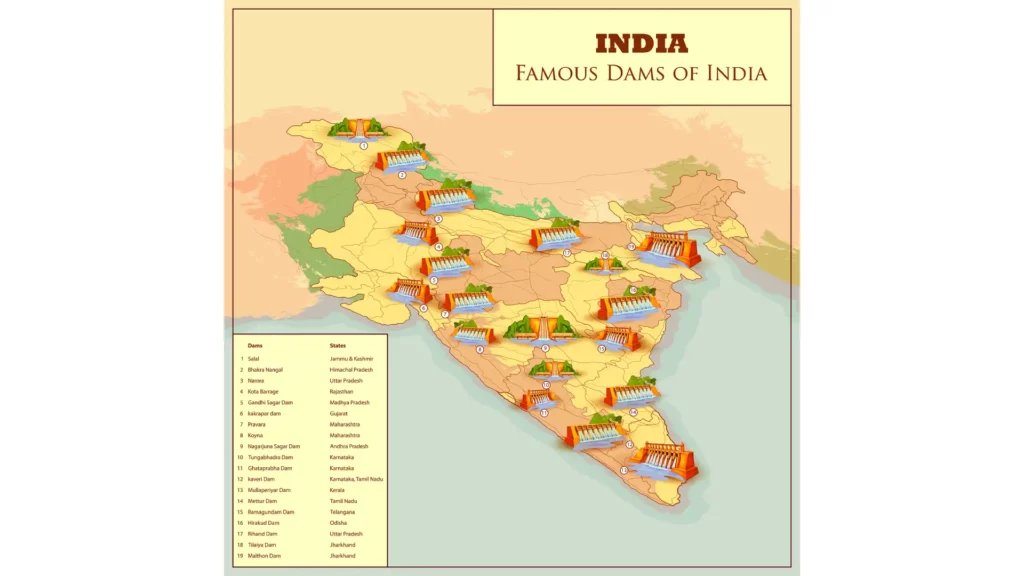
History of Hydro Energy India
The history of hydro energy India dates back to the late 19th century, with the commissioning of the first hydroelectric power plant in Darjeeling, West Bengal, in 1897, followed by the Shivanasamudra project in Karnataka in 1902.
These early projects marked the beginning of India's journey in harnessing water for electricity.
Over the decades, the country has significantly expanded its hydroelectric power capacity, with several key milestones shaping the growth of hydro energy India.
The Significance of Hydro Energy India
The importance of hydro energy India cannot be overstated. It serves as a cornerstone for achieving several critical objectives:
- Sustainability: Hydro energy is a renewable resource, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints.
- Energy Security: Enhancing India's energy security by diversifying its energy mix and reducing import dependency.
- Rural Electrification: Playing a vital role in rural electrification efforts, hydro projects often extend their benefits to remote areas, improving the quality of life.
- Water Management: Hydroelectric plants contribute to water resource management, aiding in flood control, irrigation, and drinking water supply.

The Current State of Hydro Energy India
India is a leader in hydroelectric power capacity, with plants in the north and northeast, like Tehri, Bhakra Nangal, and Nathpa Jhakri Dams.
Hydro energy plays a vital role in India's electricity generation, with a push for more projects to increase its share.
The government's support for clean energy has boosted hydro energy's growth, seen as crucial for energy security and sustainability.
Benefits of Hydro Energy India
Hydro energy offers numerous benefits, making it a key player in India's energy sector:
- Renewable and Clean: Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that reduces reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Economic Benefits: The generation of hydroelectric power creates jobs, stimulates economic growth in remote areas, and contributes to the overall development of the region.
- Energy Security: Hydro energy provides a reliable and stable source of electricity that can be ramped up or down quickly to meet demand fluctuations, enhancing India's energy security.
- Flood Control and Irrigation Support: Many hydroelectric projects offer the added benefit of flood control and irrigation support, helping to protect lands from flood damage and assisting in the agricultural development of the region.
- Water Supply: Hydroelectric plants often contribute to a region's water supply system, providing water for drinking, sanitation, and industrial uses, thereby addressing water scarcity issues.
- Recreational Opportunities: Reservoirs created by hydroelectric dams can serve as recreational spots, promoting tourism and offering activities such as fishing, boating, and swimming.
- Low Operating Costs: Once a hydroelectric plant is built, it has relatively low operating and maintenance costs compared to fossil fuel-powered plants, making it a cost-effective source of energy in the long run.

Hydro Energy in Pakistan: A Comparative Analysis
While our primary focus has been on hydro energy in India, it's also essential to briefly touch upon the state of hydro energy in Pakistan for a comparative analysis.
Like India, Pakistan boasts significant hydroelectric potential, primarily due to its proximity to the mighty Indus River and other water bodies.
However, the development and utilization of hydro energy in Pakistan face unique challenges and opportunities.
As we delve deeper into the landscape of hydro energy in India, we can draw insights and lessons that may be applicable to Pakistan's energy sector as well.
Leading Hydro Energy Companies in India
India's hydro energy sector is powered by several key players, each contributing significantly to the development and operation of hydroelectric projects across the country. Here's a summary of some of the top hydro energy companies in India:
- National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC): With over four decades of experience, NHPC is a leading player in the Indian hydro energy landscape. The company has a diverse portfolio of hydroelectric projects spread across various states, focusing on sustainable development and technological excellence.
- Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam Limited (SJVN): SJVN is renowned for its expertise in developing and operating hydroelectric power projects. The company's commitment to environmental stewardship and social responsibility is evident in its project execution, which emphasizes minimal ecological impact and maximum community benefit.
- Tehri Hydro Development Corporation (THDC): THDC, a joint venture between the Government of India and the Government of Uttar Pradesh, is known for its flagship project, the Tehri Dam. Beyond this, THDC is actively involved in other hydroelectric projects, contributing to India's energy security and socio-economic progress.
- Tata Power: While recognized for its presence in thermal and renewable energy sectors, Tata Power has also ventured into hydroelectric power generation. The company's hydro projects utilize advanced technologies for efficiency and reliability, aligning with its commitment to sustainability and innovation.
- NTPC Limited: As India's largest power utility company, NTPC has been expanding its renewable energy portfolio, including hydroelectric power generation. Through diversification and a focus on reducing carbon emissions, NTPC aims to bolster India's hydro energy capacity and meet the nation's growing electricity demands sustainably.
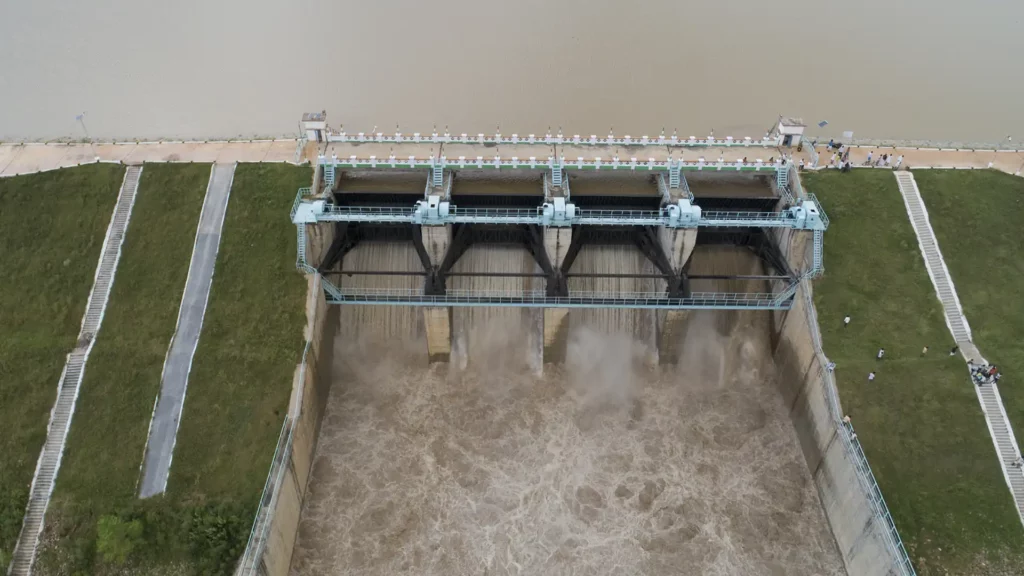

Hydro Energy India Government Policies and Initiatives
- Reclassification of Large Hydro Projects as Renewable Energy: This strategic policy shift aligns hydro energy with sustainable and green energy production goals, facilitating benefits like those available to other renewable sources.
- Introduction of Financial Incentives and Support: The government offers viability gap funding, interest subsidies, capital grants, tax incentives, duty exemptions, and accelerated depreciation benefits to make hydro projects financially viable.
- Simplification of Approval and Regulatory Processes: A single-window clearance system and streamlined environmental and land acquisition procedures reduce bureaucratic hurdles, expediting project approvals.
- Investment in Research and Development: Funds are allocated to innovate in hydroelectric technology, focusing on advanced turbine designs and smart grid technologies for better integration into the power grid.
- Promotion of Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaboration between government entities and private sector players to leverage their strengths and accelerate hydroelectric power development.
- Seeking International Collaboration and Funding: Engaging with global financial institutions and energy agencies for technical assistance, funding, and best practices in hydroelectric power development.
- Focus on Capacity Building and Skill Development: Implementing training programs and workshops to enhance the technical and managerial capabilities of professionals in the hydroelectric power industry.
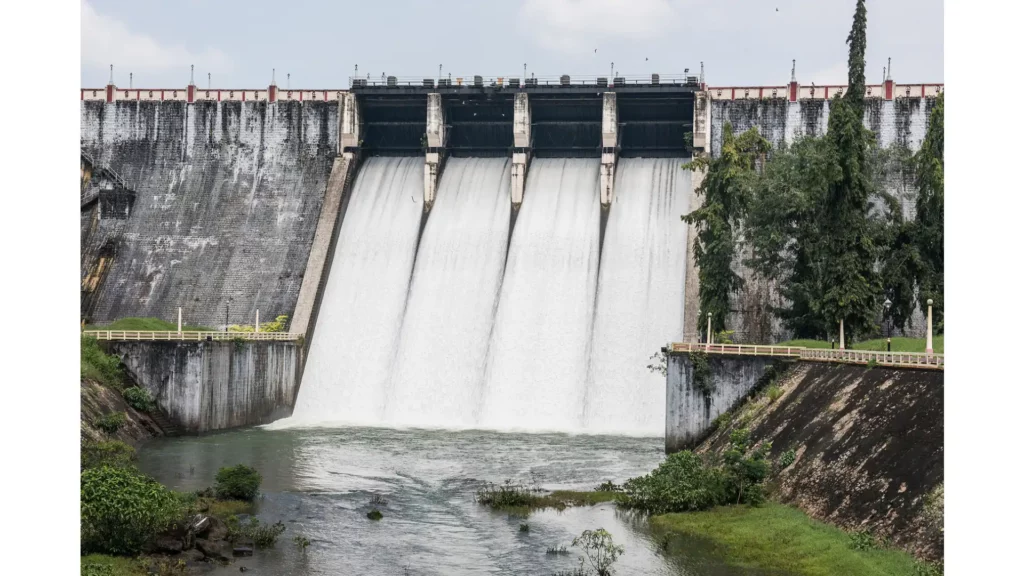

Future Prospects of Hydro Energy India
Hydro Energy India sector is set for a major transformation, shifting towards renewable resources to ensure a sustainable energy future.
Plans for capacity growth, technological advancements, and policy changes show a promising outlook.
The focus is on expanding infrastructure while prioritizing environmental protection and socio-economic progress.
- Capacity Expansion and Optimization
India plans to significantly increase hydro energy capacity, focusing on upgrading existing infrastructure for better efficiency and sustainability.
Modernizing old plants and tapping into new water resources are key aspects of this strategy.
Integrating hydro energy with solar and wind power creates a unique opportunity to develop a hybrid energy system, reshaping India's energy sector for a more resilient and sustainable future.
- Policy and Regulatory Enhancements
The Indian government is crucial in promoting hydro energy growth through policies like favorable tariffs, subsidies for small projects, and streamlined approval processes. These initiatives aim to attract investments and accelerate sector development.
- Innovations Driving Growth
Innovation drives hydro energy evolution in India, with turbine advancements and smart grid tech enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
These strides redefine hydro energy's role in India's renewable landscape, unlocking new potentials for decades ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Hydro Energy in India
1. How does hydro energy contribute to India's renewable energy goals?
Hydro energy plays a crucial role in India's renewable energy portfolio by providing a clean and sustainable source of electricity. As one of the oldest and most established renewable energy sources, hydroelectric power contributes significantly to the country's efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate carbon emissions.
2. What are the environmental impacts associated with hydro energy projects in India?
While hydroelectric projects offer numerous benefits, they also pose environmental challenges. These may include habitat disruption, alteration of river ecosystems, and potential impacts on fish populations. However, modern hydro projects often incorporate mitigation measures to minimize these effects and ensure sustainable development.
3. How does the government support the development of hydro energy in India?
The Indian government has implemented various policies and incentives to promote the growth of hydro energy. These include subsidies for small hydro projects, favorable tariff policies, and streamlined approval processes for new projects. Additionally, large hydro projects have been classified as renewable energy sources, further incentivizing investment in the sector.
4. What role do local communities play in hydro energy projects?
Local communities often play a significant role in the development and operation of hydro energy projects. Engaging with communities is essential for obtaining land access, addressing concerns related to displacement and environmental impact, and ensuring equitable distribution of project benefits. Many hydro companies in India prioritize community engagement and sustainable development initiatives as part of their project planning process.
5. How does hydro energy complement other renewable energy sources in India?
Hydro energy complements other renewable energy sources such as solar and wind by providing a reliable source of electricity generation. Unlike solar and wind, which are intermittent, hydroelectric power can be dispatched as needed, helping to stabilize the grid and ensure grid reliability. Integrating hydro with other renewables in hybrid energy systems can enhance overall energy security and resilience.
6. What are the prospects for small-scale hydro energy projects in India?
Small-scale hydro projects, often referred to as micro or mini hydro, hold significant potential in India, particularly in remote and rural areas. These projects utilize locally available water resources to generate electricity, providing sustainable energy solutions for off-grid communities. With advancements in technology and supportive government policies, the prospects for small-scale hydro projects in India are promising.
7. How can investors participate in the hydro energy sector in India?
Investors interested in participating in the hydro energy sector in India have various avenues available to them. They can invest directly in hydroelectric projects through public-private partnerships or by partnering with established hydro companies. Additionally, investors can explore opportunities in equipment manufacturing, technology development, and consultancy services related to hydro energy projects.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Hydro Energy India
The journey of hydro energy India is a testament to the country's commitment to sustainable and renewable energy sources.
With its vast potential, hydro energy stands as a beacon of hope for not just meeting India's growing energy demands but also for propelling the nation towards a greener and more sustainable future.
As we move forward, the collective efforts of the government, private sector, and communities will be paramount in realizing the full potential of hydro energy India.

