Hydroelectric Power Plants in the Philippines
As a homeowner seeking eco-friendly and sustainable energy solutions, the transformative change in the world's energy landscape presents an exciting opportunity. Hydroelectric power, a renewable source of energy, has emerged as a central player in this revolution, and fortunately, my country, an archipelago with abundant water resources, is perfectly poised to embrace this shift.
The Philippines' current state of hydroelectric power plants highlights the potential to contribute significantly to the overall energy matrix while reducing carbon footprints. As a homeowner, opting for a hydroelectric power plant becomes a viable and responsible choice to lessen my environmental impact and embrace a greener lifestyle.
Introduction to Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric is hydropower renewable, a time-honored method of harnessing energy, capitalizing on the inexhaustible force of flowing water to generate electricity. This fascinating process revolves around the conversion of the vast potential energy inherent in water at an elevated height into a dynamic cascade of kinetic energy. Through a meticulously designed system, this kinetic energy is further transformed into mechanical energy, ultimately culminating in the production of clean and renewable electrical power.
At its core, a hydroelectric is hydropower example plant operates like a grand symphony of nature and engineering. It all begins with a dam or reservoir, strategically positioned to accumulate water from rivers or streams, creating a significant height difference between the water surface and the turbines below. As water is released from the reservoir, it cascades down at high velocity, thanks to gravity, generating kinetic energy that drives massive turbines with incredible force.
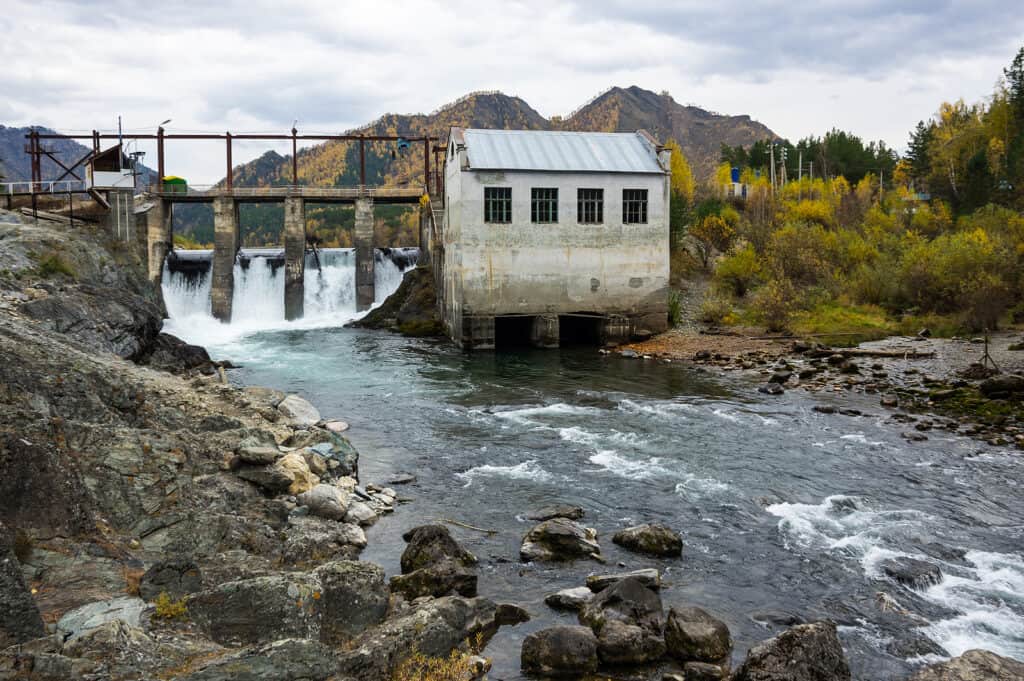
The Current State of Hydroelectric Power in the Philippines
The Philippines boasts a rich and enduring history with hydroelectric power, dating back to the early 20th century when the country commissioned its first hydroelectric plant. Over the years, this renewable energy source has flourished, and as of 2023, it is estimated that the country is home to approximately 80 operational sizes of hydroelectric power plants.
Contribution to the Energy Mix
In the dynamic landscape of the Philippines' energy sector, hydroelectric power plays a pivotal role, contributing significantly to the country's overall energy mix. As of 2022, data from the Department of Energy reveals that hydroelectric power accounted for an impressive 20% of the nation's total power generation. This substantial contribution underscores the crucial role of hydroelectricity in meeting the growing energy demands of the country's population and economy.
Geographical Distribution
The strategic deployment of hydroelectric power plants in the Philippines is closely intertwined with the nation's unique geographical features, terrain, and precipitation patterns. The archipelago's landscape, characterized by mountainous regions and abundant water resources, facilitates the establishment of hydroelectric facilities in particularly favorable locations.
The islands of Luzon and Mindanao stand out as the primary hosts of the majority of hydroelectric plants. Their rich water resources, fed by numerous rivers and ample rainfall, create ideal conditions for harnessing the power of flowing water. As a result, these regions have emerged as the epicenters of hydroelectric development in the country.
The Benefits of Hydroelectric Power in the Philippines
Hydroelectric power stands as a compelling and attractive energy source for the Philippines, offering a multitude of advantages that cater to the nation's sustainable energy goals and environmental commitments. The key benefits of hydroelectric power include:
Sustainability and Renewability
One of the foremost advantages of hydroelectric power lies in its inherent sustainability and renewability. Unlike finite fossil fuel resources, hydroelectricity draws its strength from the perpetual water cycle—a natural process driven by rain and the flow of rivers. As water constantly replenishes its sources, hydroelectric power becomes an inexhaustible and enduring energy solution, ensuring long-term energy security for the Philippines without depleting our planet's precious resources.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Embracing hydroelectric power aligns harmoniously with the Philippines' dedication to combatting climate change and fulfilling its commitments under the Paris Agreement. By employing hydroelectricity as a clean energy alternative, the country significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. In stark contrast to conventional fossil fuel-based power generation, hydroelectric plants produce minimal to negligible amounts of harmful greenhouse gases, thereby curbing the nation's carbon footprint and contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Environmental Conservation
Hydroelectric power plants are generally designed to have minimal ecological impact on their surroundings. By harnessing the energy of flowing water, these plants avoid the destructive consequences often associated with mining or drilling for fossil fuels. The construction of reservoirs might cause localized disruptions, but compared to the long-term effects of burning fossil fuels, the environmental impact is relatively small. Additionally, hydroelectric projects often offer opportunities for ecological enhancement and conservation efforts through the creation of reservoirs and the preservation of water habitats.
Energy Independence and Security
The Philippines' reliance on imported fossil fuels for energy has historically exposed the nation to the volatility of global energy markets. By embracing hydroelectric power, the country can significantly enhance its energy independence. Harnessing the vast potential of its own water resources empowers the Philippines to be less reliant on external sources of energy, mitigating vulnerability to international market fluctuations and fostering a more stable and secure energy landscape.
Reliable and Flexible Power Generation
Hydroelectric plants can be designed with storage capabilities, using reservoirs to regulate water flow and electricity generation. This provides a valuable asset in managing electricity supply and demand fluctuations, ensuring a stable and consistent power output. Hydroelectricity's flexibility also facilitates its integration into the national grid, enabling a smooth transition to cleaner energy and supporting a more resilient and efficient electricity network.
Challenges Faced by Hydroelectric Power in the Philippines
The hydroelectric power industry in the Philippines, while holding immense promise, confronts several formidable challenges that necessitate careful consideration and proactive management. These challenges encompass a range of critical issues, including:
Environmental and Social Impact
The construction of large-scale hydroelectric projects often presents complex environmental and social challenges. Such endeavors can lead to the transformation of vast areas of land, involving the creation of reservoirs and dams. Consequently, this may result in the potential displacement of communities residing in the project's vicinity. Moreover, the alteration of natural river flows and ecosystems can have cascading effects on local flora and fauna, further impacting biodiversity and ecological balance. To mitigate these concerns, comprehensive environmental impact assessments and robust community engagement are essential, seeking to strike a balance between energy development and sustainable social and environmental preservation.
Dependence on Rainfall Patterns
The efficacy of hydroelectric power plants is heavily contingent on the consistency of rainfall patterns. Adequate water flow and reservoir levels are essential to sustain optimal power generation. However, climate change, characterized by shifting weather patterns and irregular rainfall, poses a formidable challenge to the reliability of this power source. Extended periods of drought or excessive rainfall can lead to fluctuations in water availability, potentially affecting the plant's ability to maintain a steady power output. To counteract this, innovative water management strategies, such as improved storage capacity and enhanced weather prediction technologies, may be necessary to ensure a stable energy supply even in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Financing and Infrastructure Development
The establishment of hydroelectric power plants necessitates substantial initial investments in infrastructure development. Securing financing for these projects can be complex, particularly when considering their long-term nature and potential uncertainties associated with environmental and social considerations. Additionally, the geographic distribution of the Philippines' islands may pose logistical challenges, requiring extensive transmission networks to deliver the generated electricity to distant regions. Overcoming these obstacles demands well-structured financial mechanisms and comprehensive planning to optimize the overall effectiveness and accessibility of hydroelectric power.
Geopolitical and Legal Complexities
The implementation of large-scale hydroelectric projects can give rise to geopolitical and legal complexities, especially when multiple stakeholders, including neighboring countries, are involved. Shared water resources and potential transboundary impacts may necessitate diplomatic negotiations and the establishment of robust legal frameworks to govern equitable resource usage and address potential conflicts. Achieving a harmonious balance between national energy needs and international cooperation becomes vital in addressing these challenges.
Natural Disaster Resilience
Given the Philippines' susceptibility to natural disasters such as typhoons and earthquakes, ensuring the resilience and structural integrity of hydroelectric infrastructure becomes imperative. Measures to safeguard against extreme weather events and seismic activities should be integrated into the design and maintenance of hydroelectric projects to prevent potentially catastrophic consequences and uphold the reliability of this energy source.
How is Hydroelectricity Produced Step by Step
Hydroelectricity is generated by harnessing the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide on how this transformation from water to electricity occurs.
Step 1: Building a Dam
The production of hydroelectric power begins with the construction of a dam across a river. This dam creates a reservoir, storing a large amount of water at a height. The height difference, also known as the “head,” is crucial because it creates the pressure needed to drive the turbines.
Step 2: Storing Potential Energy
Once the dam is complete, water flows into the reservoir, essentially storing energy in the form of potential energy due to the water's elevation relative to the downstream water level.
Step 3: Channeling Water to the Turbines
When electricity is needed, gates in the dam open to allow water to flow out. This water is then channeled through pipes, known as penstocks, leading to the power generation facility located at the base of the dam.
Step 4: Generating Kinetic Energy
As the water rushes down through the penstock due to gravity, its potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy. The force of the moving water drives the large blades of a turbine, a device specifically designed to capture this kinetic energy and convert it into mechanical energy.
Step 5: Driving the Generator
The turbine's shaft is connected to a generator. As the turbine blades turn, they drive the generator, which is essentially a large electromagnet surrounded by wire coils. The mechanical energy from the turbine rotates the generator's rotor, creating a changing magnetic field that induces a flow of electrical current in the surrounding stator windings, thus converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Step 6: Transmission of Electricity
The generated electricity is then stepped up in voltage via transformers to be transmitted over long distances through power lines. This electricity eventually reaches homes, businesses, and industries, where it is used for numerous purposes.
Step 7: Recycle of Water
The water, after passing through the turbines, flows back into the river downstream and continues its natural course. Since the water isn't consumed during this process but merely used to transfer energy, it can be recycled and used again and again to produce electricity.
Hydroelectric Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
Hydroelectric energy is among the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy, with immense potential to contribute to the world's ever-increasing energy demand. As with any energy source, it carries both significant advantages and certain disadvantages of hydroelectric energy.
Hydroelectric Energy Advantages
1. Renewable and Sustainable
The most significant advantage of hydroelectric energy is that it's renewable. Water cycles through evaporation, rainfall, and flow back into the sea, ensuring a continual source of energy that won't deplete over time.
2. Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Compared to fossil fuels, hydroelectric power plants produce a minimal amount of greenhouse gases, contributing less to climate change. They don't release carbon dioxide or pollutants like power plants that burn fossil fuels do.
3. Reliable and Flexible
Hydroelectric power plants are reliable and offer a great deal of flexibility. They can quickly adjust to electricity demand, ramping up or down as required. This makes them suitable for meeting peak electricity demand and for providing a base load of power.
4. Long Lifespan and Lower Operation Costs
Hydroelectric power plants have a long lifespan, often exceeding 50 to 100 years. Additionally, their operation and maintenance costs are generally low compared to coal-fired or nuclear power plants.
5. Supports Other Uses
Reservoirs created for hydroelectric power plants often support other uses like recreational activities (boating, swimming), irrigation for agriculture, and drinking water supplies.
Hydroelectric Energy Disadvantages
1. Environmental and Ecological Impact
The construction of a hydroelectric power plant, particularly large-scale projects, can disrupt local ecosystems. It may lead to changes in water temperature and flow, impacting fish and other aquatic species. The construction process can also lead to habitat destruction.
2. Displacement of Communities
Building large dams and reservoirs often requires displacing local communities, causing social and economic disruptions. This can lead to numerous issues, from resettlement difficulties to conflicts over land and resources.
3. High Upfront Costs
Although the operation costs of hydroelectric power plants are relatively low, their initial construction costs can be very high. Financing such projects can be complex and challenging.
The Philippines Hydropower Potential video to understand Hydroelectric Power Plants
The Future of Hydroelectric Power in the Philippines
Despite the challenges posed by the hydroelectric power industry in the Philippines, the future of this renewable energy source shines with promise. The concerted efforts of both the government and private sector are paving the way for advancements and innovations to overcome existing obstacles and capitalize on abundant opportunities.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The Philippine government has demonstrated a keen understanding of the strategic significance of renewable energy in fostering sustainable development. With a commitment to promoting clean energy sources, including hydroelectric power, the government has instituted a series of policies and initiatives to propel the sector forward. A pivotal milestone in this endeavor is the Renewable Energy Act of 2008, a comprehensive legislation aimed at incentivizing and supporting the development and utilization of renewable energy sources across the nation. By fostering an enabling environment through supportive regulations and financial incentives, the government is spurring greater interest and investment in the hydroelectric sector.
Investment in Research and Technology
To enhance the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of hydroelectric power plants, substantial investments are being channeled into cutting-edge research and technology. A key focus area is the improvement of turbine designs, seeking to maximize power output while minimizing environmental disturbances. Researchers and engineers are exploring innovative ways to strike a balance between energy production and ecological conservation, with a keen eye on mitigating potential impacts on local ecosystems and communities. Embracing state-of-the-art technology allows the Philippines to optimize the performance of existing hydroelectric facilities and lay the foundation for future projects that exemplify environmental responsibility.
Environmental Stewardship and Mitigation
Conscious of the environmental and social challenges posed by large-scale hydroelectric projects, stakeholders are proactively pursuing mitigation measures to protect sensitive ecosystems and communities. Advanced environmental impact assessments are conducted to understand potential ramifications before undertaking construction. This approach facilitates the development of projects that respect ecological balance, mitigate impacts on biodiversity, and foster sustainable coexistence with local communities.
The Role of Mini and Micro Hydro Systems
While large-scale hydroelectric plants face their share of challenges, mini and micro-hydro systems have emerged as a compelling and environmentally friendly alternative. These smaller-scale hydroelectric facilities, designed to operate on local water resources, offer distinct advantages. They exhibit a lower environmental and social footprint, as their construction typically involves smaller reservoirs and reduced land usage. Mini and micro-hydro systems are particularly well-suited for rural and remote areas, where they can serve as decentralized sources of power, bringing electricity to communities that might be challenging to reach through conventional means.
Conclusion
As a homeowner deeply invested in finding eco-friendly and sustainable energy solutions, the journey through the world of hydroelectric power has been an eye-opening and inspiring experience. The transformative change occurring in the global energy landscape has presented an exciting opportunity to explore the vast potential of renewable energy sources, with hydroelectric power taking center stage as a key player in this revolution.
Learning about the captivating process of harnessing the force of flowing water to generate clean and renewable electricity has filled me with a sense of wonder and appreciation for the harmony between nature and engineering. The idea that the perpetual water cycle, a fundamental aspect of our planet's natural processes, can be ingeniously transformed into a sustainable and enduring energy solution is both remarkable and reassuring.

