Geothermal energy is a sustainable and renewable source of power that has been harnessed by humans for centuries. But have you ever wondered, What is the ultimate source for geothermal energy?
In this guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of geothermal energy, exploring its origins, how it works, and its environmental benefits.
What is the Ultimate Source for Geothermal Energy?
What is the ultimate source for geothermal energy? This question often comes to mind when we think about this renewable energy source.
The answer lies deep within the Earth's mantle, where heat is continuously generated through the process of radioactive decay.

How Geothermal Energy Works
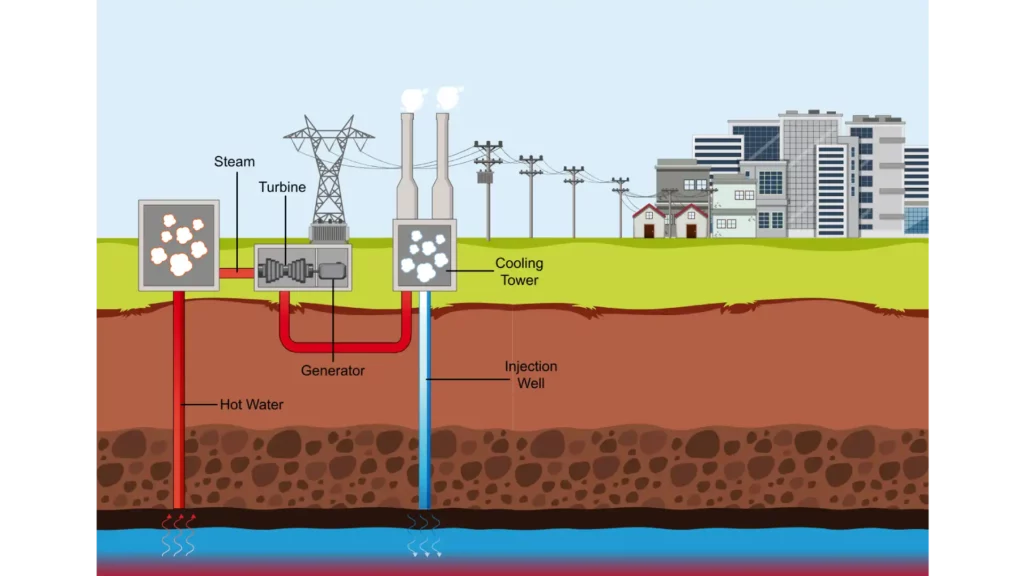
To understand what is the ultimate source for geothermal energy, we first need to grasp how geothermal energy works.
Geothermal energy is extracted by drilling wells deep into the Earth's crust, where temperatures are significantly higher than at the surface.
Water or other fluids are pumped into these wells, and the heat from the Earth causes the fluids to vaporize into steam.
This steam is then used to turn turbines, generating electricity.
The Importance of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy, harnessed from the Earth's internal heat, plays a pivotal role in meeting our energy needs. Its significance cannot be emphasized enough, as it offers a multitude of advantages for our society.
Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy is both clean and sustainable, making it a crucial pillar of our energy portfolio.
This renewable resource provides a steady supply of electricity and heating, catering to the demands of residential, industrial, and commercial sectors.

Types of Geothermal Resources
- Hydrothermal Resources: Hydrothermal resources are the most common type of geothermal resource. They involve the use of naturally occurring hot water or steam from the Earth's crust.
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS): Enhanced Geothermal Systems are engineered geothermal reservoirs created by stimulating and improving the permeability of hot rocks deep below the Earth's surface.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: Geothermal heat pumps use the stable temperature of the shallow ground to provide heating and cooling for buildings.
- GeoPressured Resources: GeoPressured resources are found in sedimentary basins where high pressure and high temperature conditions exist.
- Hot Dry Rock (HDR): Hot Dry Rock systems involve creating a geothermal reservoir in hot, impermeable rock by drilling a pair of wells.
- Magma Resources: Magma resources are associated with volcanic activity and involve harnessing the heat generated by molten rock (magma) beneath the Earth's surface.
- Low-Temperature Geothermal Resources: Some geothermal resources have lower temperatures and are used for direct heating rather than electricity generation.

Exploring the Underlying Origins of Geothermal Heat
To gain a comprehensive understanding of geothermal energy and uncover the ultimate source of this remarkable power, we must delve into the very heart of the Earth's heat generation.
The ultimate source of geothermal energy is found within the Earth's mantle, a region that stretches from the Earth's crust down to the outer core.
- The Essence of the Earth's Heat
The ultimate source of geothermal energy is a result of the ceaseless and intricate interplay of natural forces deep beneath the Earth's surface.
This process of radioactive decay is not a sudden burst of energy but rather an ongoing and inexhaustible phenomenon that sustains the Earth's internal warmth.
- The Marvel of Radioactive Decay: Earth's Inexhaustible Heat Supplier
Geothermal energy comes from the long process of decay in the Earth's mantle. Uranium, thorium, and potassium release heat energy over millions of years, giving us a sustainable source of power.
The Benefits of Geothermal Energy
The benefits of geothermal energy are numerous and contribute to its growing popularity as a sustainable and renewable energy source. Here are some of the key advantages of geothermal energy:

- Renewable and Sustainable: Geothermal energy is considered a renewable energy source because it relies on the Earth's internal heat, which is continuously replenished by natural processes.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Geothermal power production generates minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Reliable and Stable Energy Supply: Unlike some renewable sources like solar and wind, geothermal energy is available 24/7, providing a consistent and reliable source of electricity and heating.
- Energy Efficiency: Geothermal power plants have high energy conversion efficiency, typically exceeding 90%.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Geothermal energy production has a minimal environmental footprint. It does not involve the combustion of fossil fuels, which can lead to air and water pollution.
- what is the ultimate source for geothermal energyLocal Economic Benefits: Developing geothermal projects creates jobs and stimulates local economies in areas with geothermal resources.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Geothermal heat pumps for residential and commercial heating and cooling can result in significant energy cost savings over the long term.

Geothermal Energy Nonrenewable or Renewable
One of the interesting aspects of geothermal energy is the debate surrounding its classification as a renewable or nonrenewable geothermal energy source.
While it is often referred to as a renewable energy source, there are nuanced factors that warrant a closer examination of this classification.
Renewable Aspects of Geothermal Energy
- Sustainable Heat Generation: Geothermal energy is primarily generated by harnessing the Earth's natural heat, which is continuously produced through geological processes.
- Long-Term Viability: Geothermal reservoirs, which are the sources of heat for geothermal power generation, have lifespans measured in centuries or even millennia.
- Low Environmental Impact: Compared to fossil fuels, geothermal energy has a significantly lower environmental impact, emitting minimal greenhouse gases and pollutants during operation.
Nonrenewable Aspects of Geothermal Energy
- Depletion Potential: In some cases, geothermal reservoirs can be depleted or cooled down significantly faster than they naturally recharge.
- Resource Location: Geothermal energy is highly location-dependent, with the best resources concentrated in specific regions known for their geological activity.
- Energy Extraction Rate: The rate at which geothermal energy is extracted can also influence its renewable classification.
Striking a Balance
therefore can be classified as geothermal energy renewable or geothermal energy nonrenewable depending on factors like resource, management, and location. Sustainable use and responsible management are vital for its long-term viability.
Sustainable reservoir management and monitoring can maximize geothermal energy. EGS can increase availability and renewability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy stands out as an environmentally friendly and sustainable energy source. In this section, we will delve into the key factors that make geothermal energy a compelling choice in terms of its environmental impact and long-term sustainability:

- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Geothermal energy emits less harmful substances than fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gases and combating climate change effectively.
- Continuous and Renewable: Geothermal energy is a renewable resource, meaning it is continuously replenished by the Earth's internal heat.
- Minimal Land Footprint: Geothermal power plants typically require less land compared to other renewable energy sources like solar and wind farms.
- Consistent and Predictable Energy Supply: Geothermal energy is a reliable power source that enhances grid stability and energy security, unlike solar and wind energy, which depend on weather conditions.
- Reduced Water Consumption: While some geothermal power plants use water for cooling, many modern designs are water-efficient, re-injecting the water back into the reservoir to maintain sustainability. This reduces the strain on local water resources.
- Mitigation of Geothermal Fluid Disposal: Proper management of geothermal fluids is essential to prevent environmental harm. Careful reinjection and disposal practices ensure that potentially harmful substances are safely contained and do not contaminate surface water or soil.
- Preservation of Natural Hot Springs: Geothermal energy projects often coexist with natural hot springs and geothermal features. Sustainable development strategies aim to protect these valuable natural assets while harnessing the associated energy.
Future Growth Prospects
What is the ultimate source of geothermal energy future is promising thanks to advancements in technology and growing awareness of its environmental benefits.
Developing countries are increasingly turning to geothermal resources for sustainable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
International collaborations and investments are also driving exploration and development in untapped regions, setting the stage for significant market growth.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the ultimate source of geothermal energy?
The ultimate source of geothermal energy is the Earth's natural heat, primarily originating from two main processes: the heat generated during the formation of the Earth and the heat produced by the decay of radioactive isotopes within the Earth's core.
Is geothermal energy accessible everywhere?
Geothermal energy's availability depends on the geological activity of the region. It is more accessible in areas with high volcanic or tectonic activity, limiting its global reach.
How does a geothermal heat pump work?
Geothermal heat pumps use the Earth's constant temperature to provide heating and cooling. They circulate a fluid through underground pipes to exchange heat with the Earth, making them energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
Are there any environmental concerns related to geothermal energy production?
Geothermal energy is generally considered environmentally friendly. However, there can be issues related to land use, subsurface pressure changes, and the potential release of naturally occurring trace elements and minerals from geothermal fluids. Proper management and monitoring can mitigate these concerns.
Can geothermal energy completely replace fossil fuels?
While geothermal energy is a valuable renewable resource, it may not entirely replace fossil fuels due to its geographic limitations. However, it can play a significant role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
How does enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) work, and what are its advantages?
EGS involves creating fractures in hot, dry rock formations to extract geothermal energy. Its advantages include the potential to expand geothermal energy production to regions with limited natural hydrothermal resources, thus increasing accessibility.
Are there any government incentives or subsidies for geothermal energy adoption?
Many governments worldwide offer incentives, tax credits, and subsidies to promote geothermal energy adoption. These incentives aim to offset the initial installation costs and encourage the transition to clean energy sources.
What is the lifespan of a geothermal power plant?
Geothermal power plants can have a long lifespan, often exceeding 25 years. Proper maintenance and occasional upgrades can extend their operational life, making them a sound long-term investment.
Can geothermal energy be used for industrial applications?
Yes, geothermal energy can be used for various industrial processes, such as drying, pasteurization, and desalination. Its high-temperature resources make it suitable for applications requiring significant heat.
How can I determine if my location is suitable for geothermal heat pump installation?
Consult with a qualified geothermal energy expert or engineer who can perform a feasibility study. They will assess your location's geology, temperature gradient, and energy needs to determine if geothermal heat pumps are a viable option.
What is the Ultimate Source for Geothermal Energy Conclusion
In conclusion, what is the ultimate source for geothermal energy is the Earth's mantle, where heat is continuously generated through the process of radioactive decay.
This remarkable energy source has the potential to power our world sustainably, providing electricity, heating, and cooling while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As we address the challenges and continue to innovate in geothermal technology, its significance in the global energy landscape is set to grow.