Types of Biomass Energy: An Overview of the Different Forms and Their Unique Benefits
Biomass energy has been a hot topic in recent years, largely due to its potential to combat the pressing issue of climate change. This renewable source of energy holds immense potential and comes in various forms, each with its unique set of benefits. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of biomass energy and highlights their unique advantages.
What is Biomass Used For?
Biomass refers to organic materials that come from plants and animals, and it's a renewable source of energy. These materials contain energy from the sun that plants absorb through the process of photosynthesis.
When burned, the chemical energy in biomass is released as heat. Biomass can be converted into other usable forms of energy like methane gas or transportation fuels like ethanol and biodiesel.
How Does Biomass Energy Work?
Biomass energy generation works by the process of capturing the energy stored in organic materials. This energy can be converted into power in a few ways:
- Direct combustion: This is the most common method, where biomass is burned to generate heat, which is then used to heat water, creating steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator.
- Biochemical conversion: This involves the use of bacteria, enzymes, and yeast to break down the biomass into gases, liquids, or other products. An example of this is the production of biogas from anaerobic digestion or the production of bioethanol through fermentation.
- Thermochemical conversion: This involves the use of heat to trigger chemical reactions that convert biomass into gas, liquid, or solid fuel products. Pyrolysis and gasification are examples of this process.
Advantages of biomass energy
The main advantages include:
- Renewability: Biomass is a renewable resource because it can be replenished relatively quickly by growing more plants or trees.
- Carbon neutrality: Biomass is often considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released when it is burned was absorbed by the plants as they grew. Thus, it doesn't contribute to the increase of CO2 in the atmosphere, unlike fossil fuels.
- Reduction of waste: Biomass energy can make use of waste materials, such as scrap lumber, forest debris, certain crops, manure, and some types of waste residues.
- Energy security: Using local biomass resources can help to reduce dependence on foreign fossil fuels, thus improving energy security.
How can biomass energy be negative to the environment
- Deforestation: If not managed sustainably, biomass energy production can lead to deforestation and habitat loss.
- Air pollution: Burning biomass can produce air pollutants. This includes particulate matter and gases like carbon monoxide, which can harm human health.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: While biomass is often considered carbon-neutral, it's important to note that this depends on the source and how it's harvested and processed. In some cases, the entire lifecycle of biomass energy (including production, transport, and conversion) can lead to net greenhouse gas emissions.
- Use of resources: Producing biomass often requires significant water and land resources, which can lead to issues around resource scarcity and land use conflicts.
It used for
Biomass is used for several applications. It's primarily used for energy production, either through direct combustion to produce heat or via conversion to biofuels for use in vehicles. It's also used in industry, for example, to generate steam for manufacturing processes or electricity.
Besides energy production, biomass has various other uses. For instance, certain type of biomass can be processed into chemicals and materials, such as bioplastics. Additionally, biomass is often used for heating and cooking, particularly in developing countries.
Understanding Biomass Energy: A Brief Introduction
matter known as its core, biomass energy is produced from organic materials specifically plant or animal matter known as biomass. When these organic materials are broken down, they release energy that can be harnessed to create electricity, heat, or fuel. Biomass energy can be considered carbon-neutral as the carbon dioxide released during its usage is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth.
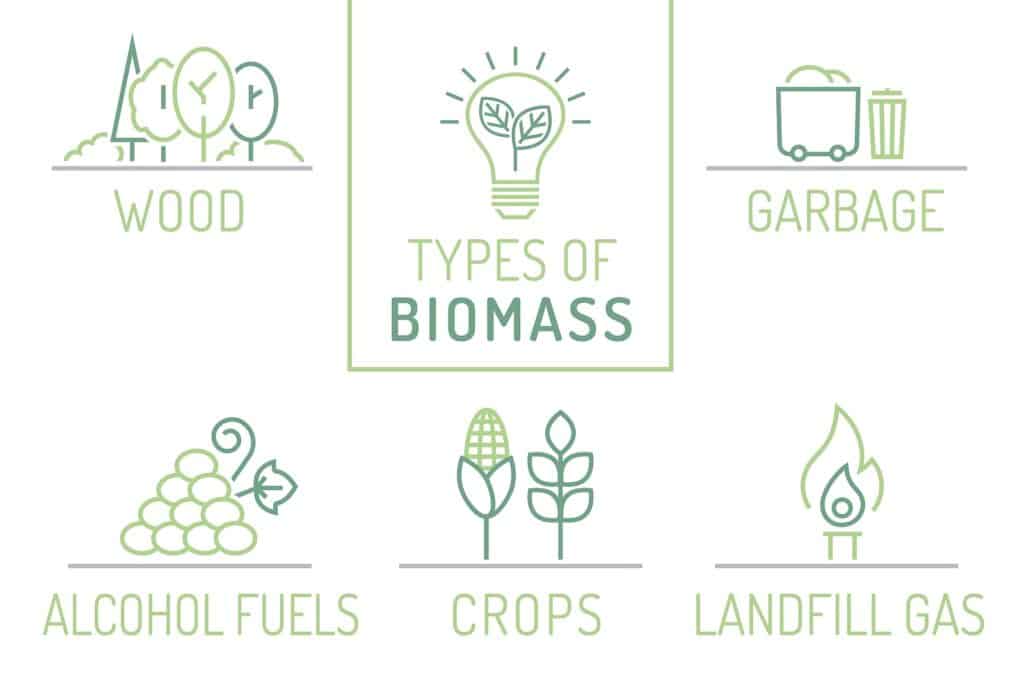
Types of Biomass Energy
There are numerous type of biomass energy, each derived from different organic materials and created using different processes. Here's a deep dive into some of the most common forms.
1. Wood and Agricultural Biomass
Wood and agricultural wastes are the most traditional and common forms of biomass. They are produced from various sources, including tree trunks, branches, leaves, crop residues, and manure. These sources of biomass can be burned directly for heat or used to produce electricity in power plants.
2. Solid Waste Biomass
Solid waste biomass refers to the organic components of municipal solid waste. It includes yard clippings, paper, and food waste. These materials can be burned to generate electricity or processed to produce biogas.
3. Landfill Gas and Biogas
Landfill gas and biogas are produced from the decomposition of organic waste in landfills or specialized digester systems. They consist mainly of methane—a potent greenhouse gas—which can be captured and used to generate electricity or heat.
4. Biofuel
Biofuel is a type of biomass energy that can be used as a substitute for traditional fossil fuels. The most common types of biofuels are ethanol and biodiesel, which can be produced from crops like corn, soybeans, and sugarcane.
5. Energy from Algae
Although still in the developmental stages, energy from biomass algae holds great. Algae grow much faster than land-based plants, and they can be harvested to produce biofuel, biogas, and other type of biomass energy.

The Benefits of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive renewable energy source.
1. Carbon Neutrality
As mentioned earlier, biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral. This is because the carbon dioxide released during the burning or decomposition of biomass fuels is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth. This helps in reducing the impact of energy production on climate change.
2. Waste Reduction
Many forms of biomass energy make use of waste materials, such as agricultural residues or municipal solid waste. By turning these materials into energy, biomass energy contributes to significant waste reduction.
3. Energy Security
Biomass energy can be produced locally, reducing dependence on foreign energy sources and contributing to energy security.
4. Economic Development
The production of biomass energy can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in farming, transportation, and energy production.
Applications of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is versatile and can be used in various applications.
1. Electricity Production
In power plants, biomass can be burned directly or co-fired with coal to produce electricity.
2. Heating
Biomass is commonly used for heating in residential and commercial buildings. This is especially true for wood and agricultural biomass, which can be burned in stoves or boilers.
3. Transportation Fuel
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can be used in vehicles, reducing the use of gasoline and diesel and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Prospects of Biomass Energy
Despite its benefits, biomass energy also has its challenges. The production of biomass energy can require significant land and water resources, and there can be environmental concerns associated with its production and use.
However, with ongoing technological advancements and increased awareness of the importance of renewable energy, the future of biomass energy looks promising. More efficient and sustainable methods of biomass energy production are being developed, and government policies are increasingly supportive of this renewable energy source.

Pioneers in Biomass Energy Production
Innovation in the field of biomass energy has been driven by pioneering companies and institutions. Here are a few notable examples:
1. BioEnergy International
BioEnergy International focuses on biofuel and biochemical production technologies. They are recognized for their commitment to creating cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
2. Pacific Biodiesel
Pacific Biodiesel is known for recycling used cooking oil into biodiesel, demonstrating an effective and sustainable method of waste repurposing.
3. Enerkem
Enerkem is acclaimed for its revolutionary method of converting municipal solid waste into biofuels and renewable chemicals, proving that even waste has immense potential in the renewable energy landscape.
Biomass Energy and Job Creation
The biomass energy industry has proven itself to be a significant driver of job creation, providing a variety of employment opportunities:
1. Biomass Cultivation
Farmers and agricultural workers who cultivate biomass crops provide the essential raw materials for biomass energy production.
2. Processing and Transportation
Workers involved in the processing and transportation of biomass materials play a crucial role in preparing and moving these resources to where they are needed.
3. Research and Development
Scientists, engineers, and technicians contribute to the ongoing innovation and development in the field of biomass energy.
Biomass Energy Policies
Government policies greatly influence the growth and development of the biomass energy industry. Here's how:
1. Subsidies and Incentives
Governments provide subsidies and incentives to stimulate the production and use of biomass energy.
2. Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks guide the safe and responsible production and use of biomass energy, ensuring that it benefits both the economy and the environment.
3. Targets and Mandates
Many governments set targets and mandates for renewable energy usage, which drive the adoption of biomass energy.
Biomass Energy vs. Other Renewable Energy Sources
While all forms of renewable energy have their unique advantages, it's worth comparing biomass energy to other renewable sources:
1. Biomass vs. Solar
Unlike solar energy, biomass energy is not dependent on weather conditions, making it a more reliable source of energy.
2. Biomass vs. Wind
While wind energy has low operational costs, biomass energy can make use of waste materials, providing a solution to waste management issues.
3. Biomass vs. Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric power can have significant environmental impacts, such as altering natural waterways. In contrast, biomass energy can be produced with minimal environmental impact when managed properly.
Public Perception of Biomass Energy
The public's perception of biomass energy can greatly influence its acceptance and adoption. Here's how:
1. Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education about the benefits of biomass energy can increase its acceptance and use.
2. Community Involvement
Community involvement in biomass energy projects can lead to increased support and positive perceptions of this renewable energy source.
3. Transparency and Communication
Transparent and honest communication about the potential impacts and benefits of biomass energy can build public trust in this renewable energy source.
Biomass Energy Sustainability Measures
The sustainability of biomass energy depends on the balance between its production and consumption. A responsible approach to biomass energy encompasses the conservation of resources, careful waste management, and the preservation of biodiversity. To achieve this balance, biomass energy producers are taking significant measures.
For instance, many producers now prioritize crop rotation practices to prevent soil nutrient depletion, ensuring that the land remains fertile and productive. They also adopt advanced irrigation systems to reduce water usage. At the same time, they carefully manage waste byproducts from biomass energy production, ensuring that these byproducts are either recycled or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
There is also an increasing focus on protecting biodiversity. Many biomass energy producers are now avoiding monoculture practices, which can negatively affect local ecosystems. Instead, they are opting to grow a mix of crops, which supports a variety of wildlife and preserves the health of the ecosystem.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Biomass Energy
Technology plays a critical role in advancing the biomass energy sector. From improving the efficiency of biomass energy production to developing new forms of biomass energy, technological innovation is at the heart of the sector's evolution.
One area where technology is having a significant impact is in the production of biofuels. Advanced technologies are being used to increase the yield of biofuels from crops, reducing the amount of land and water resources needed. For example, genetic engineering is being used to develop crops that have higher sugar contents, which can increase biofuel yield.
Another area is in the optimization of energy production from biomass. New combustion technologies are being developed that allow biomass to be burned more efficiently, generating more energy and reducing emissions. Similarly, advancements in anaerobic digestion technology are improving the production of biogas from organic waste.
Conclusion: The Future of Biomass Energy
In conclusion, biomass energy plays a critical role in the global energy landscape. With its diverse forms and unique benefits, it is an essential part of the solution to our energy and environmental challenges. As we look to the future, it's clear that biomass energy will continue to be a key player in our transition to a cleaner, more sustainable world.