Uses of Biomass Energy Harnessing Sustainable Solutions
I've been really excited about biomass energy lately, and I wanted to share some of the reasons why I think it's such a promising renewable energy source. Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, and it's gaining momentum as a fantastic environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
In this guide, I want to delve into the different ways we can use biomass energy and why I believe it has the potential to play a significant role in solving our global energy challenges, all while promoting sustainability.
What is Biomass Energy?
Biomass energy comes from organic materials, both living and dead. It includes plants and animals. This energy is renewable because it relies on substances that can be replenished quickly, like plant growth or agricultural waste.
Biomass energy is produced by burning organic materials, fermenting plants for biofuels, or using methane gas from decomposing matter. It helps reduce fossil fuel dependence, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and fighting climate change. But, its sustainability depends on managing resources carefully to balance consumption and replenishment.
Top 5 Uses of Biomass Energy
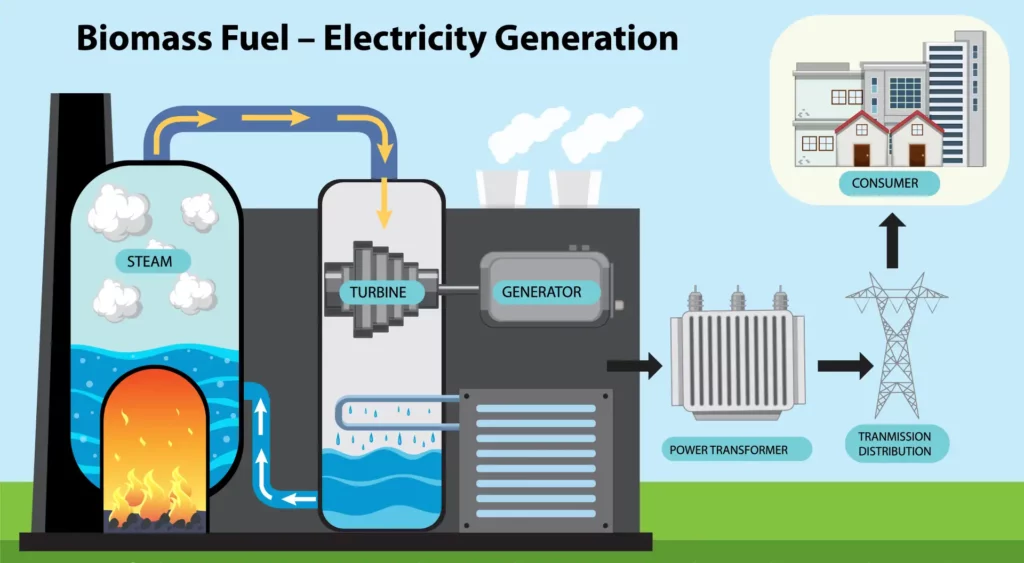
1. Electricity Generation through Biomass
Electricity generation from biomass is a key application. We delve into the methods, benefits, and challenges of biomass-to-electricity conversion.
Transforming Biomass into Electricity
Biomass can be converted into electricity through several processes:
- Direct Combustion: This involves burning biomass material, such as wood chips or agricultural waste, to produce steam. The steam then drives a turbine, generating electricity. This process is similar to how traditional power plants operate but with a renewable fuel source.
- Co-firing: Co-firing involves mixing biomass with coal in existing coal-fired power plants. This method allows for a reduction in carbon emissions without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas mixture, known as syngas, which can then be used to generate electricity. This method is more efficient and produces fewer pollutants than direct combustion.
Analyzing the Benefits and Challenges
While biomass electricity generation offers a renewable alternative with reduced emissions, it is not without challenges. The need for large land areas to grow biomass crops, water usage, and air quality concerns are significant issues. Moreover, the initial investment and maintenance costs can be high.

2. Biomass in Heating: Residential and Industrial Applications
Biomass is extensively used for heating purposes in both residential and industrial contexts.
- Biomass Heating in Homes
Wood and pellet stoves in homes provide a more sustainable and often cheaper heating solution compared to fossil fuels. These stoves can efficiently heat homes, using pellets made from compressed biomass or logs.
- Biomass in Industrial Heating
Industries use biomass in boilers to produce steam. This steam can be used for various purposes, including heating, processing, or even power generation. This application is particularly relevant in industries with access to large amounts of biomass, like agriculture or forestry.

3. Revolutionizing Transportation with Biofuels
The development of biofuels from biomass is a game-changer in reducing the transportation sector's dependence on fossil fuels.
Different Types of Biofuels
- Ethanol: Often made from corn, sugarcane, or other plants, ethanol is mixed with gasoline to reduce emissions and reliance on pure fossil fuels.
- Biodiesel: Produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease, biodiesel can replace or be mixed with regular diesel. It offers a cleaner-burning alternative to traditional diesel.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Biofuels are renewable and generally produce fewer pollutants than fossil fuels. However, their production can compete with food crops for land and water resources, raising concerns about food security and land use.

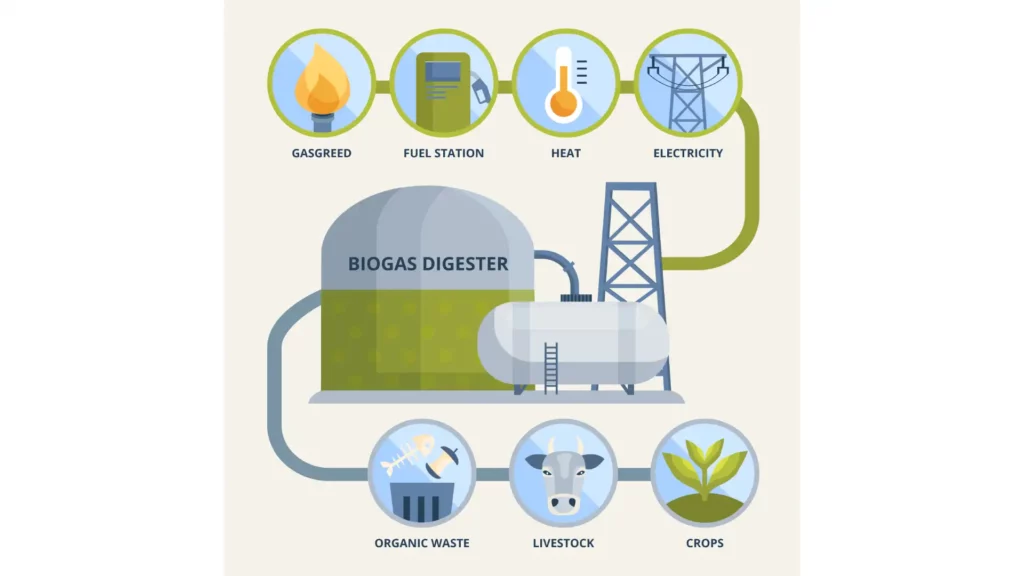
4. Biomass in Waste Management
The role of biomass energy in waste management is pivotal, transforming waste into a valuable energy resource.
- Turning Waste into Energy
Organic waste from various sources, including agriculture, forestry, and even household waste, can be converted into energy. This helps reduce reliance on landfills and cuts down methane emissions from decomposing waste.
- Embracing the Circular Economy
The circular economy model focuses on using and reusing biological materials to create a sustainable loop of energy production and waste management. This approach is crucial in reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.

5. Empowering Rural Development through Biomass
Biomass energy can have a transformative impact on rural areas, offering economic and social benefits.
Creating Employment Opportunities:
- Agricultural Sector: Biomass energy supports employment in farming, as agricultural waste and crops can be used as biomass feedstock.
- Manufacturing Industry: There's a growing demand for skilled labor in manufacturing biomass processing equipment, such as pellet mills and boilers.
- Biomass Power Plants: Opportunities arise in the operation and maintenance of biomass power plants, including roles in engineering, administration, and logistics.
- Research and Development: The biomass sector encourages research and innovation, leading to jobs in scientific research and technological development.
Boosting Energy Security:
- Reduced Dependence on Imported Fuels: Utilizing locally-sourced biomass decreases reliance on external energy sources, making rural communities more self-sufficient.
- Stable Energy Supply: Biomass provides a consistent and reliable energy source, unlike some renewable sources that are weather-dependent.
- Support for Local Agriculture and Forestry: Biomass energy promotes the utilization of agricultural and forestry by-products, providing additional revenue streams for these sectors.
Environmental Benefits:
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass energy, being part of the carbon cycle, has a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
- Waste Management: Utilizing agricultural and forestry waste for energy reduces environmental pollution and the need for landfill space.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: Sustainable biomass production can lead to better land management practices, promoting biodiversity.
Economic Diversification:
- New Markets and Industries: The biomass sector can lead to the creation of new markets, such as biofuels and bioproducts, diversifying rural economies.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in biomass energy can spur the development of infrastructure, such as transportation and energy distribution networks.
- Increased Local Investment: The growth of the biomass sector can attract more investment in rural areas, further boosting economic development.
The Importance of Biomass Energy
- Mitigating Climate Change: The adoption of biomass energy is vital in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It helps lower reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to global warming, thereby playing a crucial role in combating climate change.
- Sustainable and Renewable Source: Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, making it a more sustainable choice. Unlike finite fossil fuels, biomass can be continually replenished, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Compared to fossil fuels, biomass typically results in lower levels of pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and heavy metals, thereby reducing environmental degradation and improving air quality.
- Effective Waste Management: Utilizing biomass for energy transforms waste products, such as agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and urban waste, into valuable energy sources. This process not only reduces waste in landfills but also generates energy from materials that would otherwise be discarded.
- Economic Benefits in Rural Areas: The development of biomass energy systems can stimulate economic growth in rural areas. This includes creating jobs in the agricultural and energy sectors, fostering local industries, and encouraging sustainable agricultural practices.
- Diversifying Energy Supply: Incorporating biomass into the energy mix reduces dependence on traditional energy sources, thereby enhancing energy security and diversifying the energy supply.
- Support for Local Economies: Biomass energy production often uses local resources, which can support local economies and reduce transportation-related emissions associated with importing fuels.
- Potential for Technological Innovation: The growing interest in biomass energy can spur research and development in new technologies for more efficient and cleaner biomass conversion processes, thus continually improving its effectiveness and sustainability.

Understanding Classification of Biomass Energy
The classification of biomass energy primarily revolves around the types of Biomass Energy materials used to produce it. These materials are generally categorized based on their origin and nature.
Understanding this classification helps in determining the most efficient and appropriate use of biomass for energy production.
Types of Biomass Materials
- Woody Biomass: This includes trees, bushes, and shrubs. Woody biomass is commonly used for heat and power generation and is a staple in the production of biofuels like ethanol.
- Agricultural Biomass: This category consists of crops like corn, sugarcane, and soybeans, along with agricultural residues like straw and husks. Agricultural biomass is pivotal in the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
- Algal Biomass: Algae, though less common, is an emerging source of biomass energy. Its high yield and oil content make it a promising candidate for biofuel production.
- Waste Biomass: This includes organic waste materials such as municipal solid waste, industrial waste, and sewage. Waste biomass is often used in waste-to-energy plants to produce electricity and heat.
Importance of Classification in Biomass Energy Utilization
Understanding the classification of biomass energy is vital for several reasons:
- Optimization of Energy Production: Different types of biomass have varying energy potentials and are suitable for different energy production methods. For instance, woody biomass is ideal for direct combustion, whereas agricultural biomass is more suited for biofuel production.
- Sustainable Management: Knowing the types and sources of biomass aids in sustainable harvesting and management practices, ensuring a steady supply without harming the environment.
- Policy and Investment Decisions: For governments and investors, the classification of biomass energy provides insight into the most promising areas for investment and policy support, aligning with environmental goals and economic benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Biomass Energy
What are the Various Applications of Biomass Energy?
The application of biomass energy spans across several sectors, including electricity generation, residential and industrial heating, transportation (in the form of biofuels), and waste management. Biomass energy is applied in everyday life, notably in heating homes and powering vehicles with biofuels.
What are the Methods for Harnessing Biomass Energy?
Harnessing biomass energy involves processes like direct combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. These methods convert biomass into electricity, heat, or fuel. The choice of method depends on the type of biomass and the intended application of biomass energy.
How Do We Use Biomass Energy in Everyday Life?
Biomass energy is used in everyday life primarily through heating and transportation. Wood and pellet stoves in homes utilize biomass for heating, while biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel power vehicles, making biomass energy a part of daily commutes.
How is Biomass Energy Transported?
Biomass energy is transported in various forms, depending on its use. Solid biomass like wood chips is often transported via trucks, while biofuels are distributed through existing fuel supply chains. The transportation of biomass energy is a crucial aspect of its overall efficiency and sustainability.
Why is Biomass an Attractive Source of Energy?
Biomass is an attractive source of energy because it is renewable and has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, biomass energy utilizes waste materials, contributing to waste management, and supports rural economies, making it a sustainable and socially beneficial energy source.
Conclusion: Embracing a Biomass-Powered Future
Upon considering the vast knowledge of biomass energy, I feel hopeful and accountable for our planet's future. Biomass energy, with its various uses like generating electricity and managing waste, is crucial for a sustainable energy shift. Its ability to address both the global energy crisis and climate change is truly motivating.
Embracing biomass energy brings challenges of resource management and environmental balance. However, I see these challenges as opportunities for innovation. Adopting biomass energy means committing to a sustainable future with positive impacts on the environment and society.