In today's rapidly evolving global energy landscape, the quest for sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels has become more pressing than ever. Among the various promising solutions gaining traction in Australia biomass energy stands out as a renewable and environmentally friendly source of power.
As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and address climate change, biomass energy australia offers an avenue for Australia to make significant strides in the right direction. In this in-depth guide, we will embark on a comprehensive journey through the world of biomass energy in Australia.
We'll explore its various facets, including its definition, types of biomass energy, conversion technologies, historical context, current status, government policies, benefits, challenges, notable projects, emerging innovations, and future prospects.

Understanding Biomass Energy in Australia
Defining Biomass Energy Australia
Biomass energy represents a sustainable and environmentally friendly form of renewable energy harnessed from organic materials. These organic sources encompass a wide range of materials, including plants, wood, agricultural residues, and even municipal solid waste.
Through various intricate processes, these organic resources are transformed into usable energy, making Biomass Energy Australia a crucial component of the renewable energy landscape.
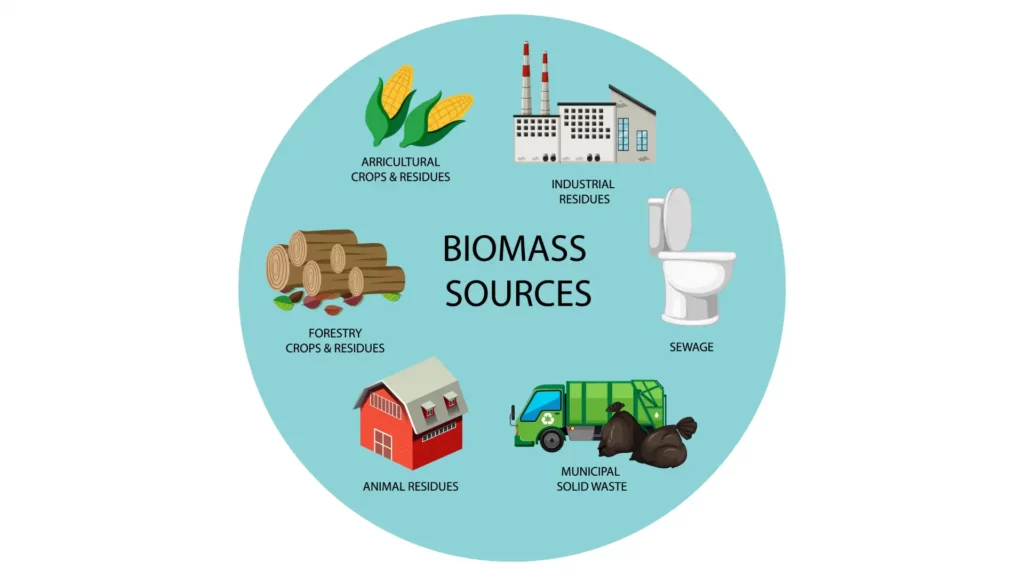
Exploring Different Biomass Sources
Biomass resources encompass a wide array of materials, each offering unique advantages and applications:
- Woody Biomass: This category consists of biomass derived from trees and woody plants, making it a time-honored source of energy in many regions.
- Agricultural Residues: Crop residues, including corn stalks, rice husks, and other agricultural waste products, represent a valuable yet often underutilized resource.
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): Converting organic waste from households and businesses into energy presents a twofold benefit.
- Animal Manure: Managing livestock waste through anaerobic digestion processes offers an eco-friendly solution to environmental challenges.
- Algae: Aquatic plants, particularly microalgae and seaweed, have garnered attention for their remarkable energy content.
Biomass Energy Australia Conversion Technologies
Biomass serves as a rich source of renewable energy, and its conversion into usable energy involves a range of sophisticated technologies. Here's a more detailed look at these Biomass Energy in Australia conversion methods:
- Combustion: This traditional biomass conversion method involves burning organic materials, such as wood, crop residues, or municipal solid waste, to produce heat.
- Gasification: Biomass gasification is a process where organic materials are thermally converted into synthetic gas (syngas) in a controlled environment with limited oxygen.
- Anaerobic Digestion: In anaerobic digestion, microorganisms break down organic matter, such as agricultural residues, sewage sludge, and animal manure, in the absence of oxygen.
- Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis is a thermal conversion process that involves heating Biomass Energy in Australia in the absence of oxygen. This results in the production of three main products:
- Bio-oil: A liquid product that can be used as a renewable fuel or feedstock for various industrial applications.
- Biochar: A solid, carbon-rich material that can enhance soil quality, sequester carbon, and be used as a filter in water treatment.
- Syngas: Similar to gasification, pyrolysis also yields syngas, which can be used for heat and electricity generation.

Biomass Energy in Australia: A Historical Overview
Biomass Energy Australia has a rich and deeply rooted history in Australia, particularly within rural communities where it served as a primary source of energy for heating and cooking throughout the early 20th century.
During this period, the utilization of wood and agricultural residues played a fundamental role in ensuring energy security in remote regions, showcasing the resilience and adaptability of biomass-based solutions.
A Modern Resurgence
Biomass energy in Australia has surged due to technology, environmental awareness, and the need for sustainable energy. It is now a crucial part of the country's energy landscape.
Policy Initiatives and Milestones
The Australian government has recognized the substantial potential of Australian biomass energy and has taken significant steps to facilitate its growth and development. Several policy initiatives and milestones have contributed to this progression:
- Renewable Energy Target (RET): The introduction of the Renewable Energy Target has been a cornerstone in the support of Australian biomass energy.
- Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA): ARENA has played a crucial role in advancing renewable energy technologies, including biomass.
- State-Level Initiatives: Several Australian states have also implemented their own policies and incentives to promote biomass energy.

The Environmental and Economic Benefits of Biomass Energy in Australia
Renewable and Sustainable Resource
One of the foremost merits of Australian biomass energy lies in its inherent renewability. Unlike finite fossil fuel sources, biomass resources can be managed sustainably through responsible forestry and agricultural practices. This ensures a continuous and abundant supply of energy while simultaneously preserving ecosystems and reducing the strain on natural resources.
Greenhouse Gas Emission Mitigation
Biomass Energy in Australia offers a unique environmental advantage when compared to fossil fuels. While the combustion of biomass does release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, this process is part of a natural carbon cycle.
Plants used for biomass energy absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during their growth, effectively offsetting the emissions produced when the biomass is burned for energy.
This carbon neutrality makes biomass energy a valuable tool in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to Australia's efforts to combat climate change.
Enhancing Energy Security and Rural Prosperity
The utilization of biomass resources for energy production serves a dual purpose of bolstering energy security and fostering rural development. By diversifying the energy mix, biomass energy reduces dependence on traditional fossil fuels, increasing the resilience of Australia's energy infrastructure.
Moreover, biomass projects have a tangible impact on local communities in rural areas. They often lead to the creation of jobs in biomass cultivation, harvesting, and processing, as well as in the operation of Biomass Energy Australia facilities.
These economic opportunities not only stimulate local economies but also contribute to the sustainable development of rural regions, providing an additional layer of benefit to Australia's overall energy and economic landscape.

Navigating Challenges and Addressing Concerns
- Resource Availability and Sustainability: A Complex Equation
Biomass energy's benefits depend on factors like responsible land use, competition for resources, and sustainable harvesting. Balancing these for a steady supply and ecological integrity is a big challenge.
- Technological Barriers and Ongoing Advances
Efficient biomass conversion tech is vital for widespread use of Aussie biomass energy. Challenges exist, but ongoing research is key to making it affordable and accessible. Innovations have potential to revolutionize Biomass Energy Australia.
- Environmental Impacts and Rigorous Mitigation Strategies
Although biomass energy is considered eco-friendly, there are still concerns. These include land use changes and the energy needed for biomass production and processing.
Effective management is crucial to minimize negative environmental effects. Mitigation strategies are necessary for sustainable biomass energy.
Efforts to improve the environmental impact of Australian biomass energy include responsible land management, efficient energy practices, and carbon sequestration initiatives.
Pioneering Biomass Energy Projects in Australia
Noteworthy Biomass Power Plants: Australia has witnessed the successful establishment of several biomass power plants, each contributing to the country's energy portfolio by harnessing the energy potential of wood waste, agricultural residues, and various organic materials.
Two standout examples include the Tumut 3 Hydroelectric Power Station and the Morwell Power Station. These projects serve as prime exemplars, illustrating the viability and advantages of biomass energy utilization within the Australian context.
Tumut 3 Hydroelectric Power Station, located in New South Wales, leverages biomass in combination with hydroelectric power generation, showcasing a hybrid approach that maximizes energy output and environmental benefits.
The Morwell Power Station, situated in Victoria, effectively utilizes biomass to generate electricity, highlighting the adaptability of biomass energy in different regions of Australia.
Emerging Innovations and Promising Initiatives: Innovation stands as a driving force behind the continuous growth of biomass energy in Australia. The country's commitment to enhancing biomass energy solutions is evident through ongoing research endeavors. These initiatives are primarily concentrated on three key fronts:
- Advanced Biomass Conversion Technologies: Researchers are actively working to develop and refine cutting-edge biomass conversion technologies.
- Exploration of New Biomass Sources: In addition to traditional biomass materials, such as wood waste and agricultural residues, Australian scientists and engineers are exploring alternative biomass sources like algae.
- Efficiency Enhancement: Ongoing efforts are dedicated to enhancing the efficiency of biomass energy systems, from biomass collection and processing to power generation.

The Bright Future of Biomass Energy in Australia
- Growth Potential in a Shifting Landscape
The outlook for biomass energy in Australia is exceedingly promising as the nation responds to the pressing challenges of climate change and the urgent need for sustainable energy sources. Biomass energy is poised to assume an ever more significant role in Australia's energy landscape.
As technological advancements continue to accelerate, and as biomass resources are managed with an unwavering commitment to sustainability, the growth potential for Australian biomass energy is nothing short of monumental.
- Synergies with Other Renewable Sources: Paving the Way for a Resilient Energy Future
Biomass energy stands as a vital complement to other renewable sources such as wind and solar power. It provides a unique advantage by offering consistent and dispatchable power, filling the gaps when intermittent renewables face limitations.
The integration of Biomass Energy Australia with these sources represents a key strategy in enhancing the reliability and stability of Australia's renewable energy systems.
This synergy not only ensures a seamless transition toward a greener and more sustainable future but also reinforces the nation's commitment to a diversified and resilient energy landscape.
Australia's embrace of renewable energy includes biomass energy, wind, and solar power. These sources will shape the nation's energy future.
Biomass Energy in Australia: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the current contribution of biomass energy to Australia's energy mix?
As of our latest knowledge update in January 2022, biomass energy contributes a small but growing share of Australia's energy mix. It accounts for approximately 2% of the country's total electricity generation. However, it's worth noting that this figure may have changed since then due to ongoing developments in the energy sector.
How does biomass energy impact Australia's carbon emissions?
Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide (CO2) released during combustion is roughly equivalent to the CO2 absorbed by the biomass during its growth. Therefore, biomass energy can help reduce net carbon emissions when it displaces fossil fuel-based energy sources. It plays a valuable role in Australia's efforts to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
What types of biomass resources are most commonly used in Australia?
In Australia, woody biomass, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste are among the most commonly used biomass resources for energy generation. Woody biomass, sourced from trees and woody plants, is particularly prevalent in biomass power plants.
Are there any incentives or government programs to support biomass energy projects in Australia?
Yes, the Australian government has implemented several incentives and programs to support biomass energy projects. These include the Renewable Energy Target (RET), the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), and various state-level renewable energy schemes. These initiatives provide financial support and incentives to promote the growth of renewable energy sources, including biomass.
What are the key challenges in expanding biomass energy production in Australia?
Expanding biomass energy production in Australia faces challenges such as resource availability and sustainability, technological barriers, and concerns about environmental impacts. Ensuring a consistent and sustainable supply of biomass resources while addressing these challenges is crucial for the industry's growth.
How can biomass energy complement other renewable energy sources in Australia?
Biomass energy can play a complementary role in Australia's renewable energy landscape by providing a consistent and dispatchable power source. When integrated with intermittent renewables like wind and solar, biomass energy can help stabilize the grid and ensure a reliable supply of electricity, especially during periods of low renewable energy generation.
Are there any notable biomass energy projects or innovations in Australia that we should be aware of?
Yes, Australia has several notable biomass energy projects, including the Tumut 3 Hydroelectric Power Station and the Morwell Power Station, which utilize wood waste for electricity generation. Additionally, ongoing research efforts are exploring emerging innovations, such as advanced biomass conversion technologies and the utilization of algae and agricultural residues for energy production.

Biomass Energy in Australia Conclusion
In conclusion, biomass energy in Australia holds immense potential as a sustainable, renewable, and environmentally friendly source of power. While challenges and concerns exist, the ongoing dedication to research, development, and policy support is likely to propel biomass energy projects across the nation.
As Australia strives to reduce carbon emissions and transition towards a greener future, Biomass Energy Australia will undoubtedly play a pivotal and enduring role in achieving these crucial goals.
The journey towards a sustainable energy future begins with a thorough understanding of the opportunities and challenges of biomass energy in Australia. By harnessing the power of biomass, we can collectively contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable, and environmentally responsible energy landscape for generations to come.
See also our in-depth post about the types of biomass energy
Source
https://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/energy/resources/other-renewable-energy-resources/bioenergy